An implementation of seminal CVPR 2016 paper: "A Hierarchical Deep Temporal Model for Group Activity Recognition."
- Key Changes
- Key Takeaways
- Demo Preview
- Installation
- Dataset
- Ablation Study
- Evaluation Metrics & Observations
- Usage
- Model Deployment
| Paper | Year | Original Paper | Original Implementation | Key Points |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CVPR 16 | 2016 | Paper | Implementation | Two-stage hierarchical LSTM for group activity recognition |
-
Improved Baselines: Updated baseline implementations with better network architectures, e.g., using ResNet50 instead of AlexNet.
-
higher accuracies were achieved in all baselines compared to the paper. Specifically, our final baseline achieved an accuracy of 93%, whereas the paper reported 81.9%.
-
A new baseline(Baseline9) was introduced that achieved 92% accuracy without the need for a temporal model.
-
Modern Framework: Re-implemented in PyTorch instead of Caffe.
-
Fine-Tuned YOLOv8 for Player Detection: To increase the labeled dataset and improve deployment for player detection, achieving 97.4% mAP50.
| Baseline | Accuracy (Paper) | Accuracy (Our Implementation) |
|---|---|---|
| B1-Image Classification | 66.7% | 78% |
| B2-Person Classification | 64.6% | skipped |
| B3-Fine-tuned Person Classification | 68.1% | 76% |
| B4-Temporal Model with Image Features | 63.1% | 81% |
| B5-Temporal Model with Person Features | 67.6% | skipped |
| B6-Two-stage Model without LSTM 1 | 74.7% | 81% |
| B7-Two-stage Model without LSTM 2 | 80.2% | 88% |
| B8-Two-stage Hierarchical Model(1 group) | 70.3% | 89.2% |
| B8-Two-stage Hierarchical Model(2 groups) | 81.9% | 93% |
| B9-Fine-Tuned Team Spatial Classification | New-Baseline | 92% |
- Higher Baseline Accuracy: Significant improvements in baseline accuracy, achieving up to 93% compared to the original paper's 81.9%.
- Modern Framework: Re-implemented the model in PyTorch, offering a more modern and flexible framework compared to the original Caffe implementation.
- New Baselines Introduced: Added new baselines, such as Baseline9, which achieved 92% accuracy without a temporal model.
- Comprehensive Ablation Study: Detailed ablation study comparing various baselines, highlighting the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches.
- Hierarchical Temporal Modeling: Utilized a two-stage hierarchical LSTM to effectively capture both individual and group dynamics.
- Team-Aware Pooling: Implemented team-wise pooling to reduce confusion between left and right teams, improving classification performance.
- Extensive Dataset: Provided a comprehensive volleyball dataset with annotated frames, bounding boxes, and labels for individual and group activities.
- Configurable Parameters: YAML-based configuration for easy adjustment of model parameters.
- Early Stopping and Visualization: Built-in mechanisms for early stopping and metric visualization, including confusion matrices and classification reports.
- Scalable and Modular Design: Designed the project with a scalable and modular structure for easy expansion and maintainability.
- Fully Deployed & Interactive Testing: The model is deployed on Hugging Face Spaces using Streamlit, allowing users to upload videos or images and test the model in real-time through a web interface.
-
Clone the repository:
git clone /~https://github.com/MohamedLotfy989/Group_Activity_Recognition_Volleyball.git cd Group_Activity_Recognition_Volleyball -
Install the required dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txt
We used a volleyball dataset introduced in the aforementioned paper. The dataset consists of:
- Videos: 55 YouTube volleyball videos.
- Frames: 4830 annotated frames, each with bounding boxes around players and labels for both individual actions and group activities.
|
|
- Training Set: 2/3 of the videos.
- Train Videos: 1, 3, 6, 7, 10, 13, 15, 16, 18, 22, 23, 31, 32, 36, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 48, 50, 52, 53, 54.
- Validation Set: 15 videos.
- Validation Videos: 0, 2, 8, 12, 17, 19, 24, 26, 27, 28, 30, 33, 46, 49, 51.
- Test Set: 1/3 of the videos.
- Test Videos: 4, 5, 9, 11, 14, 20, 21, 25, 29, 34, 35, 37, 43, 44, 45, 47.
The dataset is available for download at GitHub Deep Activity Rec, or on Kaggle here
- Multiple Baselines: Baseline1, Baseline3, Baseline4, Baseline5, Baseline6, Baseline7,Baseline8, and Baseline9.
- Configurable Parameters: YAML-based configuration for easy adjustments.
- Early Stopping: Built-in mechanism to halt training if no improvement is observed.
- Metric Visualization: Includes confusion matrices and classification reports.
- Scalable Design: Modular structure for future expansion and maintainability.
-
Description: Fine-tunes ResNet50 on entire frames classification without temporal information.
-
Insights: Works well for static image classification but lacks sequential understanding.
-
Key Features: Frame-level classification, no temporal context.
-
Description: Fine-tunes ResNet50 on person classification before extracting and pooling features for group activity recognition.
-
Insights: classification by focusing on individual actions but still lacks temporal modeling.
-
Key Features: Person-level classification, pooled feature extraction.
-
Description: Introduces LSTM for temporal modeling while still relying on image-level features.
-
Insights: Adds sequential understanding but lacks structured representation of players.
-
Key Features: LSTM for temporal learning, image-based feature extraction.
-
Description: Removes the person-level LSTM while keeping scene-level lstm modeling but relying on person-level features.
-
Insights: Scene-level modeling helps understand global activity but loses fine-grained player-level details.
-
Key Features: Scene-level LSTM, no player-level temporal learning, person-based feature extraction.
-
Description: Removes the scene-level LSTM but keeps player-level LSTM.
-
Insights: Retains individual player dynamics but struggles with global activity understanding.
-
Key Features: Player-level LSTM, no scene-level temporal modeling.
-
Description: Uses both player-level and scene-level LSTMs for hierarchical temporal modeling.
-
Insights: Effectively captures both individual and group dynamics.
-
Key Features: Hierarchical LSTM architecture, structured team dynamics.
-
Description: Adds team-wise pooling before applying scene-level LSTM.
-
Insights: Reduces confusion between left and right teams, improving classification.
-
Key Features: Team-wise pooling, hierarchical scene modeling.
-
Description: Fine-tunes ResNet50 on individual player actions before pooling team representations.
-
Insights: Achieves state-of-the-art accuracy by leveraging fine-grained person representations.
-
Key Features: ResNet50-based person classification, Team-wise pooling, optimized scene classification.
This table outlines the progression of different baseline models, highlighting their implementation improvements and accuracy as measured in our implementation.
| Baseline Model | Baselines Implementation | Accuracy (Our Implementation) |
|---|---|---|
| B1 - Image Classification | Fine-tune ResNet50 On Image Level → Classify group activity. | 78% |
| B2-Person Classification | Extract person features(ResNet50 without Fine-tune) → Pool features over players → Classify group activity. I passed this baseline because it doesn't fine-tune. | N/A |
| B3 - Fine-tuned Person Classification | Fine-tune ResNet50 on Cropped Person Actions → Extract features → Pool features over players → Classify group activity. | 76% |
| B4 - Temporal Model with Image Features | Based on B1 → Extract image features → Apply LSTM for temporal modeling → Classify group activity. | 80% |
| B5 - Temporal Model with Person Features | Based on B2 → Apply LSTM for player-level modeling → Pool features → Classify group activity. I passed this baseline since I passed B2, and same idea applied in B7 | N/A |
| B6 - Two-stage Model without LSTM 1 | Based on B3 → Extract person features → Pool features → Apply LSTM for scene-level modeling → Classify group activity. | 81% |
| B7 - Two-stage Model without LSTM 2 | Based on B3 → Extract person features → Apply LSTM for player-level modeling → Pool features → Classify group activity. | 88% |
| B8 - Two-stage Hierarchical Model | Based on B3 → Extract person features → Apply LSTM for player-level modeling → Pool features over players → Apply LSTM for scene-level modeling → Classify group activity. | 89.20% |
| B8 - Two-stage Hierarchical Model with Team Pooling | Based on B7 → Extract person features → Apply LSTM for player-level modeling → Pool features per team → Concatenate Both Teams → Apply LSTM for scene-level modeling → Classify group activity. | 93% |
| B9 - Fine-Tuned Team Spatial Classification | Fine-tune ResNet50 on Cropped Person Actions → Extract player features → Pool features per team → Classify group activity. | 92% |
- Baseline 1 → 3: Early models focus on frame-based CNN classification before shifting to person-level classification.
- Baseline 4 → 5: Introduces LSTM-based temporal modeling for both image and player-level features.
- Baseline 6 → 7: Evaluates the effects of removing person-level or scene-level LSTMs.
- Baseline 8 → 9: Moves toward hierarchical team-aware pooling and an end-to-end structured classification approach.
- L-set and r-set recognition reached 92% recall, benefiting from scene-level representations.
- Pass actions remain a weak point (r-pass at 65% recall), showing that removing person-level LSTM impacts individual action recognition.
- Balanced macro and weighted accuracy scores, indicating overall improvement in scene-level understanding.
- R-winpoint performance jumped to 83% recall, meaning the model is now effectively distinguishing game-ending actions.
- Pass recognition significantly improved (l-pass: 96%, r-pass: 90% recall) compared to earlier baselines.
- Spike actions remain highly distinguishable (l-spike: 89%, r-spike: 90%), indicating robust temporal modeling.
- Winpoint actions are weaker (l_winpoint: 79%, r_winpoint: 64%), suggesting some confusion in game-ending states.
- Strong macro and weighted averages (~88%), proving that hierarchical structure helps even without scene-level LSTM.
- Pass actions maintain strong recognition (r-pass: 94% recall), improving from B7.
- Winpoint classification improves (l_winpoint: 77%, r_winpoint: 84%), reducing confusion in match-ending events.
- Balanced performance across all actions (~90% f1-score for most classes).
- Team interactions are still not explicitly modeled, leaving room for improvement.
- Highest overall performance so far, with a macro average of 93%.
- Team-aware pooling significantly improves winpoint actions (l_winpoint: 92%, r_winpoint: 93%).
- Better precision-recall balance across all activity classes.
- Spike and pass actions remain dominant at 92–96% accuracy, indicating the success of structured representation.
- Minimal misclassification, highlighting the model’s strong team-aware learning.
- Very close to B8 with Team Pooling in overall performance (92%).
- Winpoint recognition is the strongest (l_winpoint: 94%, r_winpoint: 95%), showing optimal game state classification.
- Pass and spike actions maintain high precision and recall, ensuring smooth team-based action understanding.
- Final structured hierarchical learning approach proves highly effective, confirming the best possible performance.
- Pass action recognition improves consistently, peaking at ~96% recall in B8 with Team Pooling.
- Winpoint classification struggles in early models but reaches 95% in B9, proving the importance of structured team representation.
- Spiking actions remain robust across all baselines, with minor refinements from B7 onward.
- Hierarchical modeling (B7,B8) yields the best results, demonstrating the effectiveness of structured feature learning.
- Team pooling (B8 with team separation) plays a crucial role in reducing left/right confusion and boosting final performance.
To train a specific baseline model, execute the corresponding script:
python scripts/train_baseline1.py
python scripts/train_baseline3/train_phase_1_fine_tune.py
python scripts/train_baseline3/train_phase_2_feature_extraction.py
python scripts/train_baseline3/train_phase_3_group_classifier.py
python scripts/train_baseline4.py
python scripts/train_baseline6.py
python scripts/train_baseline7.py
python scripts/train_baseline8_v1.py
python scripts/train_baseline8_v2.py
python scripts/train_baseline9.pyYou can download the features and checkpoints from here.
Model configurations are stored in the configs/ directory. Adjust parameters such as learning rate, batch size, and number of epochs by editing the relevant .yml file.
Evaluation is performed automatically after training. Results include metrics like confusion matrices and classification reports, which are saved in the runs/ directory.
Logs and model outputs are organized into timestamped folders within the runs/ directory for easy tracking of experiments.
This model has been deployed using Streamlit and Hugging Face Spaces, allowing users to test the model directly in a web interface. You can upload a ** a video**, and the model will detect players, extract features, and classify the group activity.
🔹 Frameworks Used for Deployment:
- Streamlit → Frontend UI for testing the model interactively.
- Hugging Face Spaces → Hosting the app for easy access.
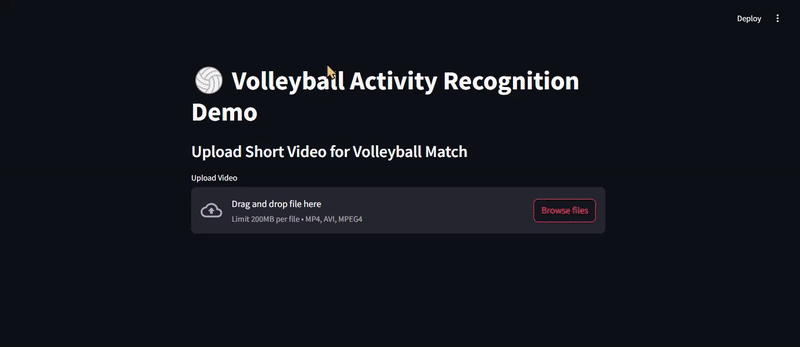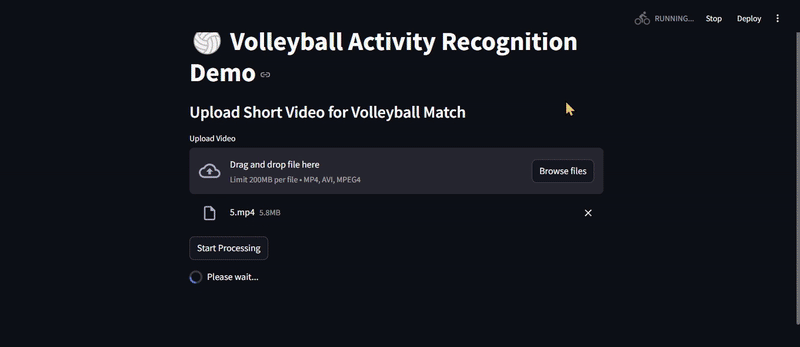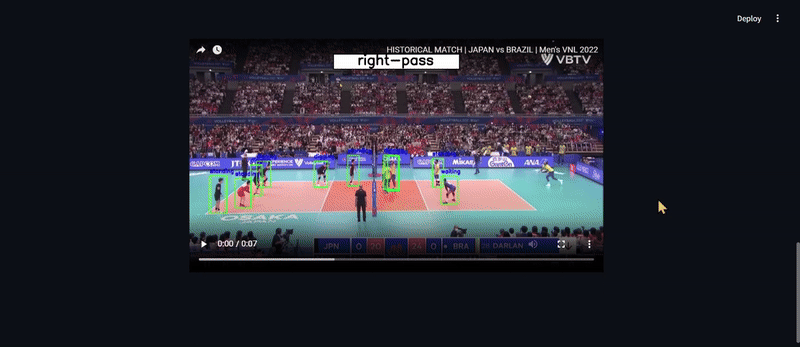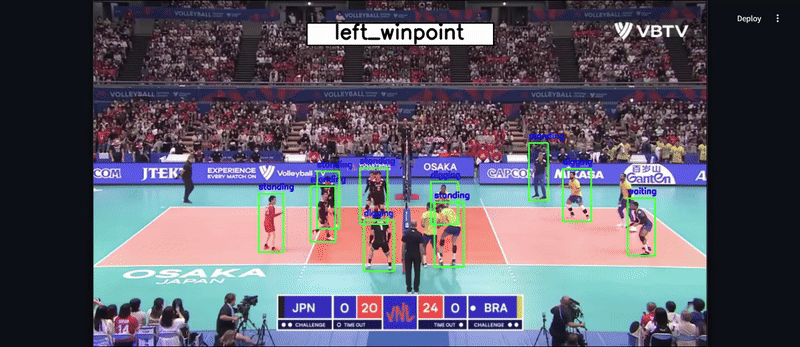
1️⃣ Player Detection: YOLOv8 fine-tuned on volleyball data (97.4% mAP50 accuracy). 🏆
2️⃣ Feature Extraction: A deep feature extractor encodes player movements.
3️⃣ Activity Recognition: A Hierarchical LSTM model predicts the group activity.
We have deployed a Volleyball Activity Recognition model that you can test right now! 🎯
🔹 Upload a Short video for volleyball match
🔹 The model will detect players, extract features, and classify the group activity.
🔹 If you upload a video, the app will overlay predictions on it!
Click the button below to test it yourself:
1️⃣ Click on the button above to open the app.
2️⃣ Upload
- A video file (MP4, AVI, etc.)
3️⃣ The model will process the input:
- 🔍 Detects players using YOLOv8
- 🎭 Extracts player features using a Feature Extractor
- 🏆 Predicts the group activity using LSTM
4️⃣ Results will be displayed on the screen.
5️⃣ For videos, the model will overlay predictions on the video, and you can download the processed video.