This workshop was insprired by - How to create a Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard & Map App in React with Gatsby and Leaflet by Colby Fayock
The Coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic has swiftly changed how all of us interact day to day. How can we use available APIs to build a mapping app that shows the impact it has had on the world?
- What are we going to build
- What do we need before we get started
- Step 1: Cleaning up some unneeded code
- Step 2: Fetching the Coronavirus data
- Step 3: Transform the Coronavirus data into a geographic data format
- Step 4: Adding the Coronavirus data to the map
- Step 5: Turn our static map into auto updated map
- Step 6: Add extra info
- Step 7: Mobile view
- Step 8: Deploy with netlify and SSR issues in Gatsby
We’ll be putting together a mapping application that uses an API containing recent Coronavirus statistics and maps out the locations and impact each country is facing.
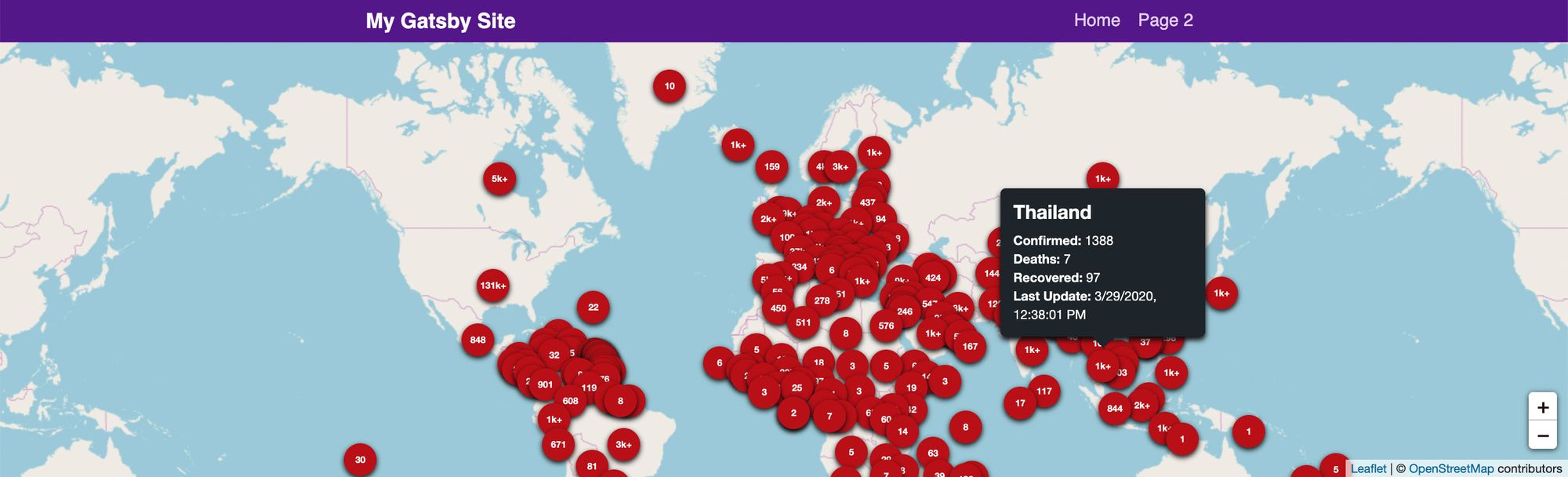
 On the map, we’ll show a marker for each country with the number of confirmed cases. On top of that, we’ll include a little popup tooltip that shows more in depth information.
On the map, we’ll show a marker for each country with the number of confirmed cases. On top of that, we’ll include a little popup tooltip that shows more in depth information.
The map we’ll build will mostly look like the above, but will look a little simpler. We’ll utilize the OpenStreetMap public tileserver.
To get started, we’re going to use this Leaflet Gatsby Starter which has been created by Colby Fayock to make the initial setup a little smoother. With our app bootstrapped, we’ll fetch our data and add markers to the map with our data.
- node or yarn - you can choose whatever suites you best
- Gatsby’s CLI -
npm install -g gatsby-clioryarn global add gatsby-cli
We’ll also want to set up a foundation for our map. We can do this by utilizing the Leaflet Gatsby Starter which provides us a basic setup with Leaflet and React Leaflet.
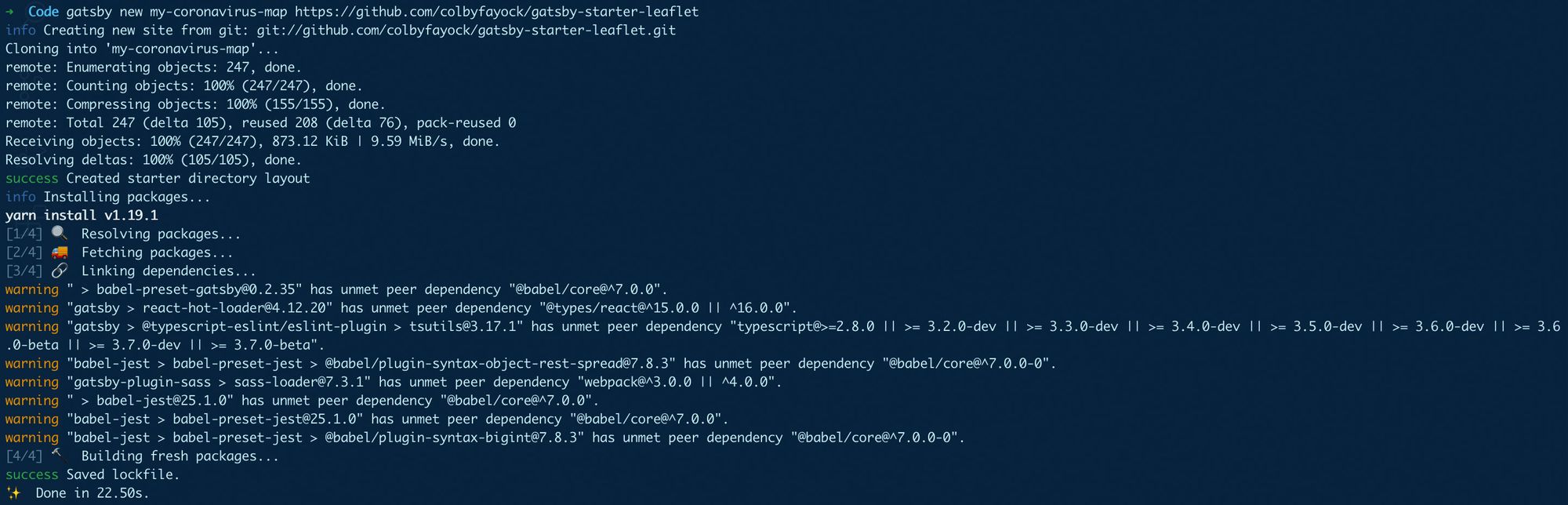
gatsby new my-coronavirus-map /~https://github.com/colbyfayock/gatsby-starter-leafletAfter that’s finished running, you can navigate to the newly created project directory and start your local development server:
cd my-coronavirus-map
npm run developIn case of error
```shell
enerating development JavaScript bundle failed
Missing binding /Users/ariell/Projects/coronavirus/new/my-coronavirus-map/node_modules/node-sass/vendor/darwin-x64-64/binding.node
Node Sass could not find a binding for your current environment: OS X 64-bit with Node.js 10.x
Found bindings for the following environments:
- OS X 64-bit with Node.js 12.x
This usually happens because your environment has changed since running `npm install`.
Run `npm rebuild node-sass` to download the binding for your current environment.
File: src/assets/stylesheets/application.scss
failed Building development bundle - 6.447s
```
In that case run
```shell
npm rebuild node-sass
```
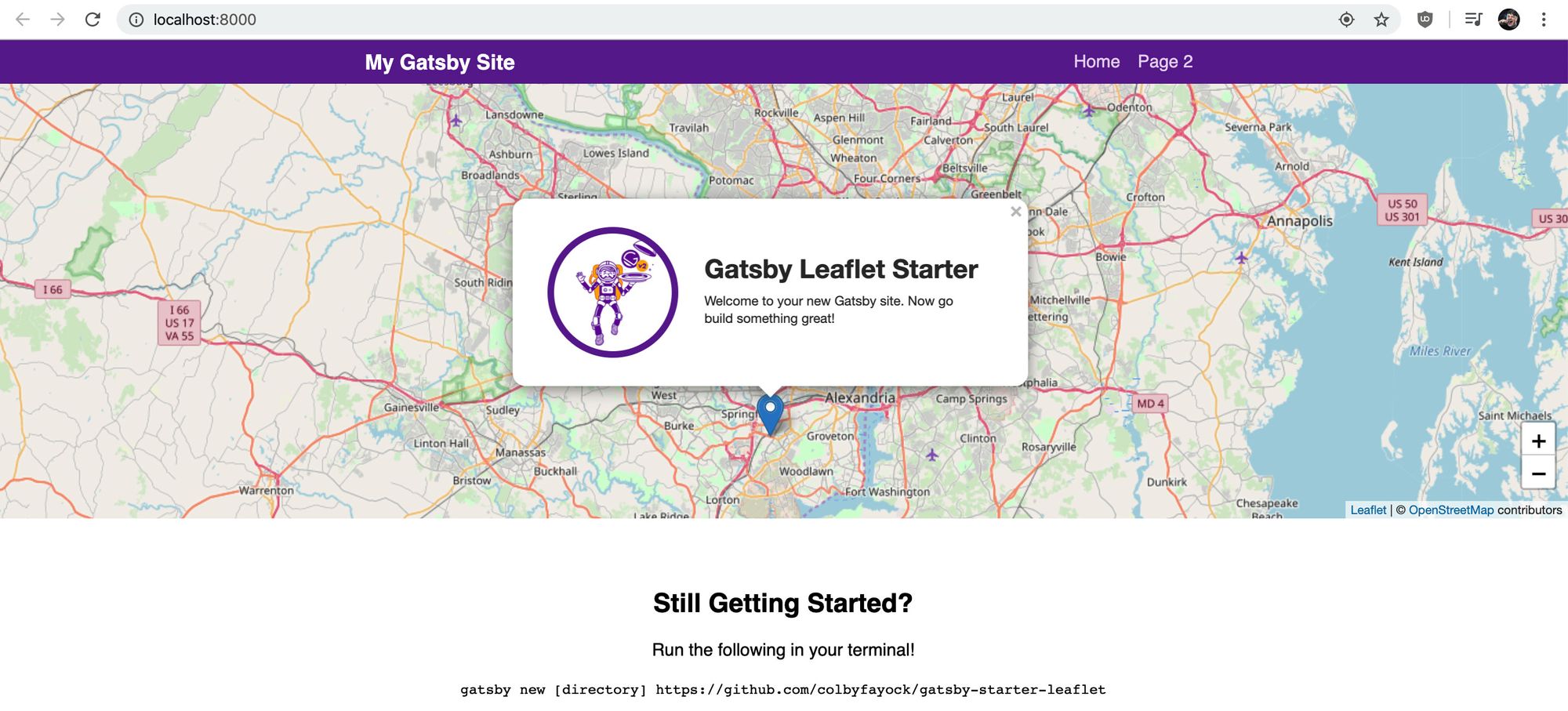
If all goes as planned, your server should start and you should now be able to see your basic mapping app in your browser!
The Gatsby Starter project we're using to spin up this app comes with some demo code that we don’t need here. We’ll want to make all of the changes below in the file src/pages/index.js, which is the homepage of our app.
First, let’s remove everything from the mapEffect function. This function is used to run code that fires when the map renders.
// In src/pages/index.js
async function mapEffect({ leafletElement } = {}) {
// Get rid of everything in here
}We’ll also change the variable name of our leafletElement simply for being able to more easily understand the code as we write it.
async function mapEffect({ leafletElement: map } = {}) {
}Next, we don’t want a marker this time, so let’s remove the <Marker component from our <Map component:
<Map {…mapSettings} />
Now that we have those pieces cleared out, we can remove all of the following imports and variables from the top of our file:
- useRef
- Marker
- promiseToFlyTo
- getCurrentLocation
- gatsby_astronaut
- timeToZoom
- timeToOpenPopupAfterZoom
- timeToUpdatePopupAfterZoom
- ZOOM
- popupContentHello
- popupContentGatsby
- markerRef
After, our map should still work, but not do anything.
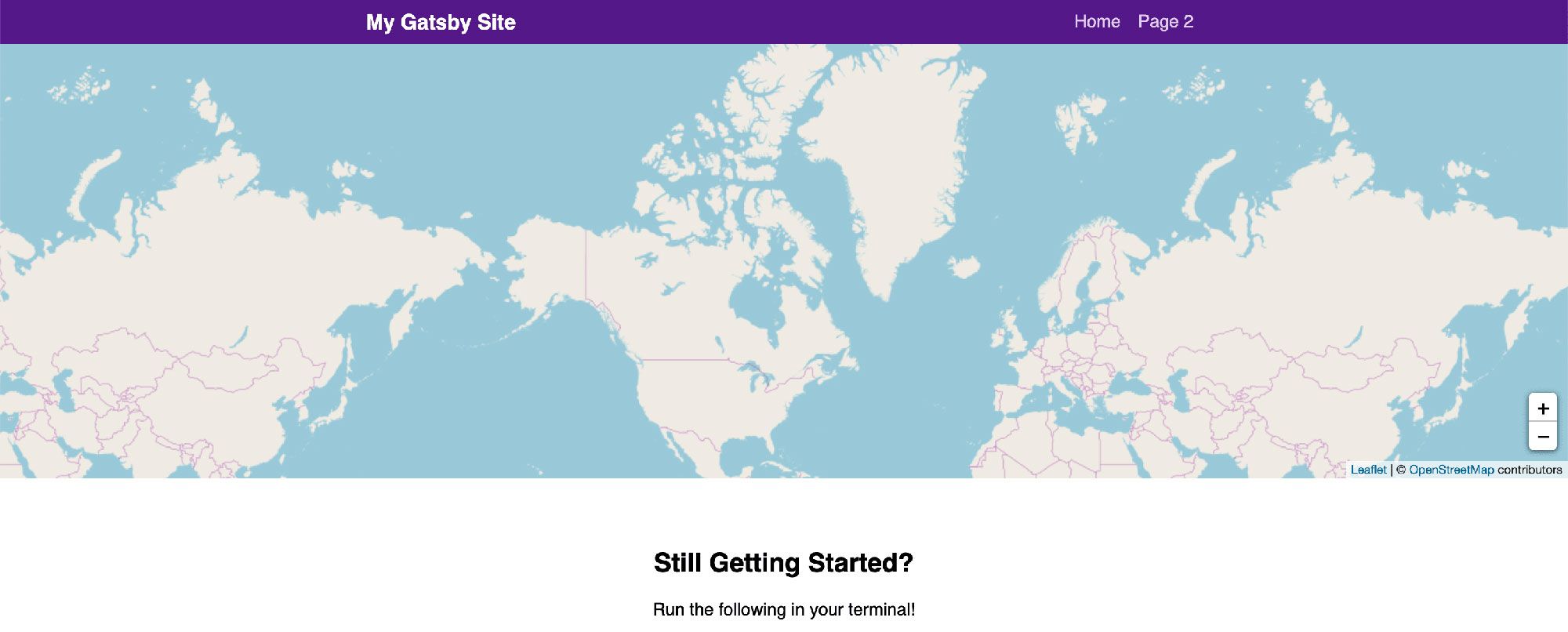
Now you might be wondering why it doesn't appear to be centering properly. Go ahead and change the LOCATION variable at the top of the index.js file to:
const LOCATION = {
lat: 0,
lng: 0
};Once that’s set, when the page reloads, the map should be centered in the middle of the world!
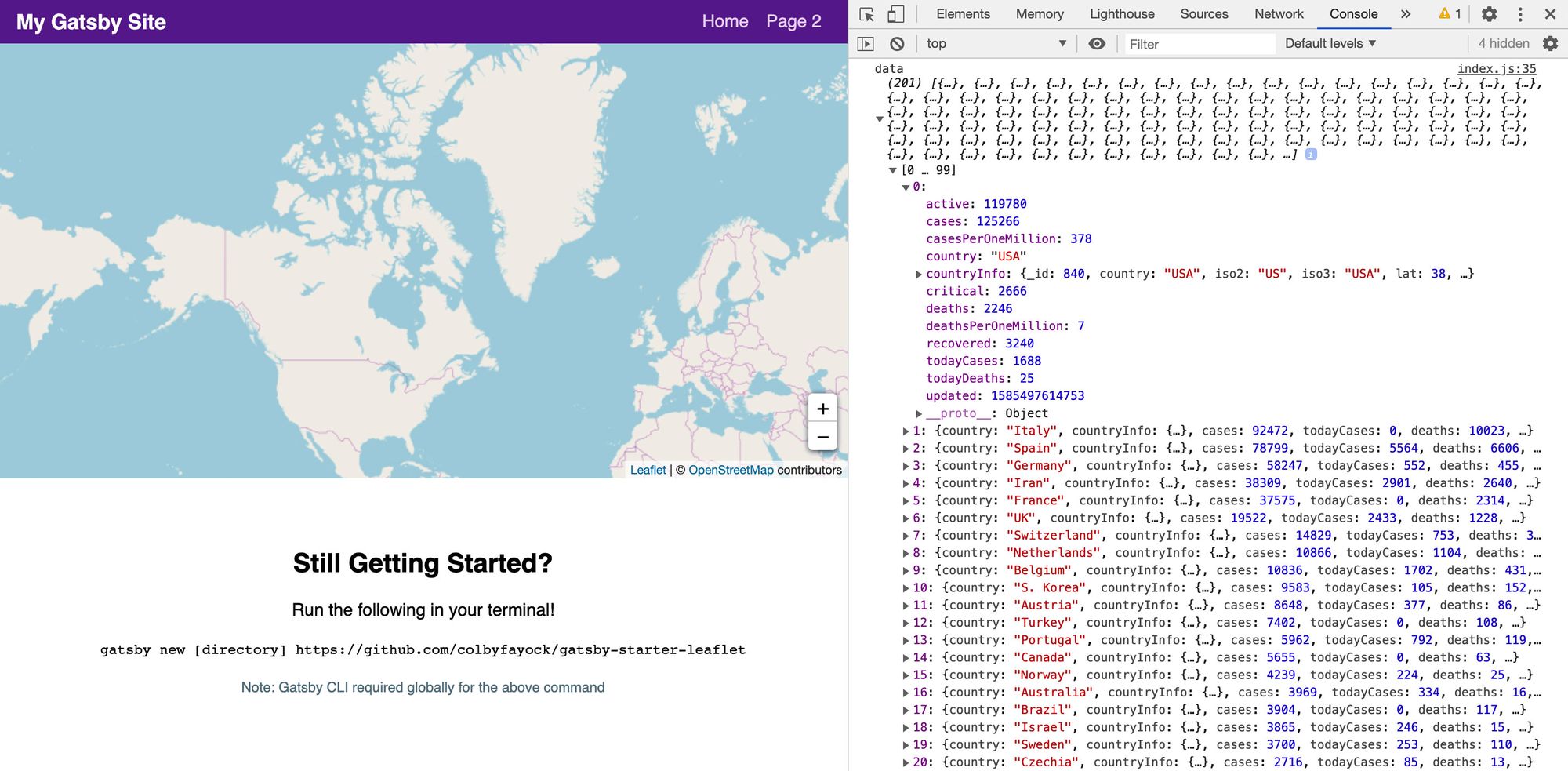
For our app, we’re going to use the NovelCOVID API. Particularly, we’re going to use the countries endpoint to fetch the list of our countries and the stats associated with them.
For making requests, let's use axios . If you want to use fetch or your own favorite request library, substitute that in for this step.
We’ll start by installing axios:
npm install axiosOnce that installs, remember to restart your server.
Import the axios package at the top of our pages/index.js file:
import axios from 'axios';Next we’ll make our request. Inside our mapEffect function, let’s try to make a request to the API endpoint:
async function mapEffect({ leafletElement: map } = {}) {
let response;
try {
response = await axios.get(`https://corona.lmao.ninja/v2/countries`);
} catch(e) {
console.log('Failed to fetch countries: ${e.message}', e);
return;
}
const { data = [] } = response;
}In this snippet, we’re doing the following:
- Setting up a
responsevariable that will allow us to store the response - Adding a
try/catchblock that will catch any API errors if the request fails - If the request is successful, we store the response in the
responsevariable - If the request fails, we console log out the error and return out of the function so we don’t continue to run the code with a failed request
- Once we have our response, we can destructure
datafrom the response and set the default value to an empty array, as that will be the type of data we need
After that’s set up, we can console log out the data object and we’ll see our data successfully fetched!
Now that we have our data, we can transform it into a geographic data format, particularly GeoJSON, that will allow us to interface with Leaflet.
Let’s start by adding this block of code to our mapEffect function:
const { data = [] } = response;
const hasData = Array.isArray(data) && data.length > 0;
if ( !hasData ) return;
const geoJson = {
type: 'FeatureCollection',
features: data.map((country = {}) => {
const { countryInfo = {} } = country;
const { lat, long: lng } = countryInfo;
return {
type: 'Feature',
properties: {
...country,
},
geometry: {
type: 'Point',
coordinates: [ lng, lat ]
}
}
})
}So what are we doing here?
- We create a new constant called
hasDatathat checks if ourdatavariable is an array and has data - If we don’t have data, we want to return out of the function, as we don’t want to try to add data we don’t have
- We create a
geoJsonobject that will be our GeoJSON document - Our document is of type
FeatureCollectionand as ourfeatureswe loop through our dataset - For each country in our data, we obtain the
latandlngto create a point for our map - We additionally add our country data as properties so we can access it within our mapping APIs
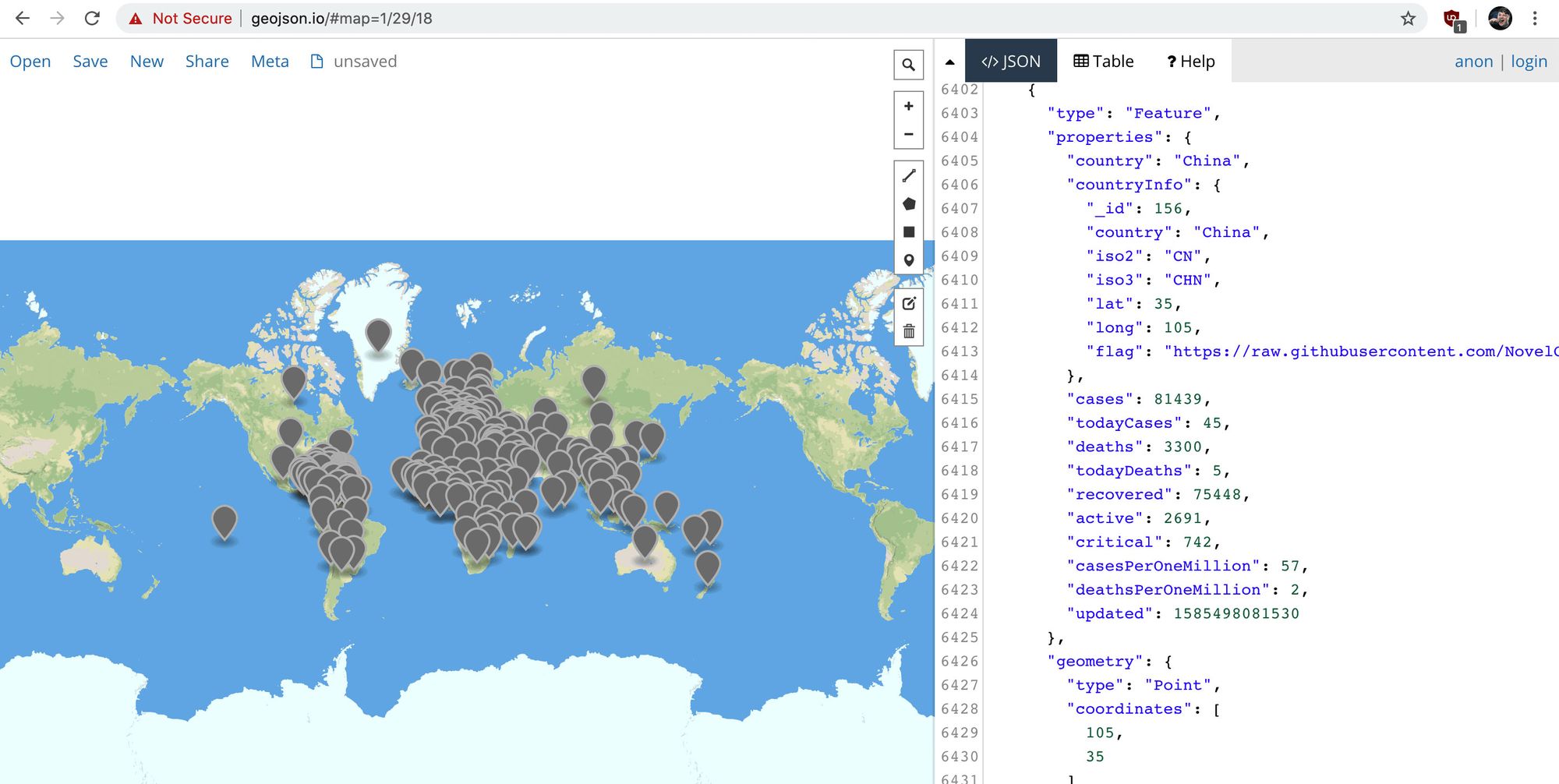
If you console.log this object into your browser and copy the contents, you can paste this into geojson.io and see the location data show up correctly.
With this GeoJSON document, we'll now be able to add it to our map.
We have our GeoJSON document with our location data, so let’s add it to the map.
Let’s start by adding this code block to our mapEffect function. It's a long one, but we’ll break it down piece by piece:
const geoJsonLayers = new L.GeoJSON(geoJson, {
pointToLayer: (feature = {}, latlng) => {
const { properties = {} } = feature;
let updatedFormatted;
let casesString;
const {
country,
updated,
cases,
deaths,
recovered
} = properties
casesString = `${cases}`;
if ( cases > 1000 ) {
casesString = `${casesString.slice(0, -3)}k+`
}
if ( updated ) {
updatedFormatted = new Date(updated).toLocaleString();
}
const html = `
<span class=“icon-marker”>
<span class=“icon-marker-tooltip”>
<h2>${country}</h2>
<ul>
<li><strong>Confirmed:</strong> ${cases}</li>
<li><strong>Deaths:</strong> ${deaths}</li>
<li><strong>Recovered:</strong> ${recovered}</li>
<li><strong>Last Update:</strong> ${updatedFormatted}</li>
</ul>
</span>
${ casesString }
</span>
`;
return L.marker( latlng, {
icon: L.divIcon({
className: 'icon',
html
}),
riseOnHover: true
});
}
});So what are we doing here?
- We create a new instance of
L.GeoJSONwhich will transform our GeoJSON document into something Leaflet will understand - Inside that instance, we define a custom
pointToLayerfunction. This allows us to customize the map layer Leaflet creates for our map - In our function, we assign and create our datapoints that we want. Most of it is destructuring, but we format the cases count to show
1k+instead of1000and a formatted date instead of the timestamp - We create an HTML string block which is used to define our map marker that will be added to the map. This also includes the HTML for the tooltip that will pop up when hovering over a marker
- We return
L.markerwith our custom configuration that includes a class oficonfor the container and our custom HTML. - Additionally, we add the
riseOnHoverproperty so when hoving over a marker, it surfaces itself above over the other markers on the map
We also want to add a bit of CSS here so that we can make sure our markers show up in the map and are usable. Let’s add this snippet to our assets/stylesheets/components/_map.scss file:
.icon-marker {
display: flex;
position: relative;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
color: white;
width: 3.6em;
height: 3.6em;
font-size: .7em;
font-weight: bold;
background-color: $red-800;
border-radius: 100%;
box-shadow: 0 2px 5px rgba(black, .9);
&:hover {
.icon-marker-tooltip {
display: block;
}
}
}
.icon-marker-tooltip {
display: none;
position: absolute;
bottom: 100%;
width: 16em;
font-size: 1.4em;
padding: 1em;
background-color: $blue-grey-900;
border-radius: .4em;
margin-bottom: 1em;
box-shadow: 0 3px 5px rgba(black, .9);
&:before {
display: block;
position: absolute;
bottom: -.6em;
left: 50%;
content: '';
width: 1.4em;
height: 1.4em;
background-color: $blue-grey-900;
transform: rotate(45deg);
margin-left: -.7em;
}
h2 {
font-size: 1.5em;
line-height: 1.2;
margin-bottom: .1em;
margin-top: 0;
}
h3 {
font-size: 1.2em;
margin: .1em 0;
font-weight: normal;
color: $blue-grey-100;
}
ul,
p {
font-weight: normal;
}
ul {
list-style: none;
padding: 0;
margin: .6em 0 0;
}
}What we’re doing:
- We create our round markers using the
.icon-markerclass and set up our.icon-marker-tooltipclass to show up when hovered over - Our
.icon-marker-tooltipclass is hidden by default, as it’s our tooltip, but we position it absolutely to appear over top of our marker and formatted the way we want it
And finally, once we have our geoJsonLayers created with our styling added, we can add it to the map!
geoJsonLayers.addTo(map);
If you followed along, you now have created your own Coronavirus map dashboard that gives some quick stats about the cases around the world.
also we are going to - add a column with extra info, a bit of style and mobile view, so we could access it from any where
So our NovelCOVID API is being updated every 10~ minutes.
There are many ways of implementing update mechanism for our map, we are gonna do polling.
The first thing comes to my head when someone says polling mechanism is - Interval.
We gonna do it with java script basic method SetInterval
we will need to fire mapEffect function every duration we will choose, for developing and debuging we will use small duration of 2000 miliseconds.
We will wrap setInterval in hook.
It will be a costume hook which will be called useInterval.
lets create js file with the name useInterval, and insert this block of code
import React, { useEffect, useRef } from 'react';
function useInterval(callback, delay) {
const savedCallback = useRef();
// Remember the latest callback.
useEffect(() => {
savedCallback.current = callback;
}, [callback]);
// Set up the interval.
useEffect(() => {
function tick() {
savedCallback.current();
}
if (delay !== null) {
let id = setInterval(tick, delay);
return () => clearInterval(id);
}
}, [delay]);
}
export default useInterval;
This hook was suggested and written by Dan Abramov. Here is a blog post I recommend by Dan Abramov about it. It explains the hook benefits and why using setInterval just doesn’t work as you’d expect - Making setInterval Declarative with React Hooks
Now lets add the call for the hook in our code, go to Map.js file
under useRefEffect add this line of code :
useRefEffect({ ref: mapRef, effect: mapEffect });
useInterval(() => mapEffect(mapRef.current),2000);
also refactor useRefEffect
const useRefEffect = ({ effect, ref = {} }) => {
useEffect(() => {
effect( ref.current );
}, [ref]);
};
useRefEffect will catch the first update, then useInterval will be set, and will trigger mapEffect function each interval.
Now all left to do is to update index.js file and mapEffect function:
lets add let geoJsonLayers = {}; next to const DEFAULT_ZOOM = 2;
we also need to install lodsah:
npm i --save-dev lodashOnce that installs, remember to restart your server.
Import the lodash package at the top of our index.js file:
import _ from "lodash";also add this block of code above IndexPage function
export const updateMap = (geoJsonLayersData, map) => {
if (!_.isEmpty(geoJsonLayers)) {
geoJsonLayers.clearLayers();
}
geoJsonLayers = geoJsonLayersData;
geoJsonLayers.addTo(map);
};
So what are we doing here?
In case of update we will want to clear the map from all the dots and draw new ones. we will save geoJsonLayers from interval to interval from now.
Now lets refactor mapEffect function, replace
geoJsonLayers.addTo(map)
with
updateMap(geoJsonLayers, map);
That's it , now you map is not static anymore 🎉
Well your map is no longer static, but there are to many points for you to notice 🌐 Let's change it !
In NovelCOVID API there are lots of info that until now we didn't use, for this section we will get :
- total confirmed cases over the world
- date of Last time our data was updated in NovelCOVID API
lets start with adding another call to NovelCOVID API (and a bit of refactoring)
In index.js file, replace this block of code:
let response;
try {
response = await axios.get(‘https://corona.lmao.ninja/v2/countries’);
} catch(e) {
console.log('Failed to fetch countries: ${e.message}', e);
return;
}
const { data = [] } = response;with this block of code :
let countriesResponse, totalsResponse;
try {
[countriesResponse, totalsResponse] = await Promise.all([
axios.get("https://corona.lmao.ninja/v2/countries"),
axios.get("https://corona.lmao.ninja/v2/all")
]);
} catch (e) {
console.log(`Failed to fetch: ${e.message}`, e);
return;}
const { data: countriesData = [] } = countriesResponse;
const { data: totalsData = {} } = totalsResponse;Also replace any data variable with countriesData
So what are we doing here?
we added another call to NovelCOVID API, and warrped both of them with Promise.all
now what are we going to do with all of this data we got ?
We will create new component Section, it will render column with three parts.
Let's create Section.js file under components directory
For start, add this block of code in the new file :
import React from 'react';
export const Section = () => {
return (
<section className="section-left">
<p>Corona Virus Map</p>
</section>
);
};
export default Section;
now we will render Section in Layout component
In Layout component, replace return section with this block of code :
<>
<Helmet bodyAttributes={{ class: className }}>
<title>Gatsby Site</title>
</Helmet>
<div className="wrapper">
<Header />
<div className="main-screen">
<Section />
<main className="main">{children}</main>
</div>
</div>
</>
In application.scss file add this block of style code:
.wrapper {
min-height: 100vh;
display: flex;
height: 100%;
flex-direction: column;
}
.column {
height: 100%;
display: flex;
}
.header {
display: flex;
flex-shrink: 0;
flex-direction: row;
}
.header-left {
flex-grow: 2;
}
.header-right {
flex-grow: 20;
}
.main-screen {
flex-grow: 1;
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
}
.section-left {
flex-grow: 1;
max-width: 300px;
}
.main {
flex-grow: 3;
}and remove
main {
padding: 2em 0;
}In index.js file, replace return section with this block of code , it will make our map prettier
return (
<Layout pageName="Corona Virus Map">
<Helmet>
<title>Corona Virus Map</title>
</Helmet>
<Map {...mapSettings} />
</Layout>);
now if you suppose to see column in the left side of the map :
Because Section in rendered inside Layout we can't pass the data from index to Section without prop drilling,
In that case lets use context
In index file add this line of code :
export const TotalsContext = React.createContext(null);
Inside indexPage function add this :
const [totals, setTotals] = useState({});
const [countries, setCountries] = useState({});
Inside mapEffect function , after we got the data and this lines of code :
setTotals(totalsData);
setCountries(countriesData);
and finally lets warrp Layout component in index.js like this
<TotalsContext.Provider value={{ totals, countries }}>
.
.
.
.
.
.
</TotalsContext.Provider>
So what are we doing here?
we created TotalsContext with React.createContext function, we initiate it with null.
Then we added usage of setState hook for totals and countries, and update both of them after we are get the data from the NovelCOVID API.
finally we warped our Layout component with TotalsContext.Provider and passed the data there, so we could access it in Section component directly.
Now back to Section.js file , we need to add this line of code :
const { totals, countries } = useContext(TotalsContext) || {
totals: {},
countries: {}
};
It uses useContext hook to get data and updates from TotalsContext
Don't forget to import {TotalsContext} from '../pages'; and useContext hook
because we are going to handle a lot of number changes, lets use react-odometerjs to make the transitions look pretty
npm install --save-dev react-odometerjsOnce that installs, remember to restart your server.
Now it's time to refactor Section component
Add this block of code after useContext hook :
if (typeof window === "undefined" || !window.document) {
return <div />;
}
const dtf = new Intl.DateTimeFormat("en-US", {
year: "numeric",
month: "short",
day: "2-digit",
hour: "2-digit",
minute: "2-digit",
hour12: true
});
let d = "...";
const totalCases = !_.isEmpty(totals) ? +totals.cases : 0;
if (!_.isEmpty(totals)) {
const date = new Date(totals.updated);
d = dtf.format(date);
}
const sortedCountries = _.sortBy(
!_.isEmpty(countries) ? countries : [],
country => country.cases
).reverse();
Replace Section return section with this block of code :
return (
<section className="section-left">
<div className="box totals">
<h3>Total Confirmed</h3>
<div className="total-number">
<Odometer value={totalCases} duration={500} format="(,ddd)" />
</div> </div> <div className="box countries">
<h3>Confirmed Countries cases</h3>
{!_.isEmpty(sortedCountries) &&
sortedCountries.map(country => {
if (country.country !== "World") {
return (
<React.Fragment key={country.country}>
<ul className="countries-item">
<li className="country-title"
>
{`${country.country} `}
</li>
<li className="country-cases">
<Odometer value={country.cases}
duration={500}
format="(,ddd)"
/>
</li> </ul> </React.Fragment> );
}
})}
</div>
<div className="box last-update">
<h3>Last Update</h3>
<p>{!_.isEmpty(totals) ? `${d}` : "..."}</p>
</div>
</section>);
What left to do is to create _Section.scss file in stylesheets/components folder :
section {
&.section-left {
background-color: #e0e0e0;
text-align: center;
}
&.section-left:after {
content: "";
opacity: 0.5;
top: 0;
left: 0;
bottom: 0;
right: 0;
position: absolute;
z-index: -1;
}
.box {
background-color: #fbfbfb;
margin: 4px 4px;
border-radius: 5px;
border: 1px solid #bfbdbd;
padding: 5px 0;
box-shadow: 0 1px 3px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.12), 0 1px 2px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.24);
transition: all 0.3s cubic-bezier(0.25, 0.8, 0.25, 1);
}
.box:hover {
box-shadow: 0 14px 28px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.25), 0 10px 10px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.22);
}
.box:last-child{
padding: 0;
}
.total-number {
margin: 10px 0;
font-size: 40px;
}
.countries {
overflow: scroll;
max-height: 63vh;
.countries-item {
list-style-type: none;
display: block;
padding: 0 2.5em 10px 2.5em;
border-bottom: 1px solid #bfbdbd;
text-align: start;
.country-title {
display: inline-block;
padding-right: 5px;
}
.country-cases {
display: inline-block;
color: red;
}
}
}
}In __components.scss file add an import :
@import "section";In Section.js add these imports:
import "assets/stylesheets/application.scss";
import "odometer/themes/odometer-theme-default.css";
check that you didn't forget to import all the new packages !
now you suppose to see our upgraded map 🎉
Becasue a Map app that can't be used at your phone is not really a map app, lets add a quick style fixes so it would look great also in our phone 📱
Let's refactor application.scss
Add this line of code inside .main-screen class
@media (min-width: 320px) and (max-width: 480px) {
flex-direction: column-reverse;
}Add this line of code inside .section-left class
@media (min-width: 320px) and (max-width: 480px) {
max-width: 100%;
}Add this line of code inside .main class
@media (min-width: 320px) and (max-width: 480px) {
height: 60vh;
}Let's refactor _map.scss
under .icon-marker add
&.mobile-active {
@media (min-width: 320px) and (max-width: 480px) {
display: block;
}
}one last thing - we lost the hover effect , it's mobile and we don't have it anymore
lets replace it, should work with click in mobile
in index.js inside mapEffect function, in html variable add class - icon-marker-tooltip-${country} to the element
<span class="icon-marker-tooltip icon-marker-tooltip-${country}">
instead of return L.marker we will save it like this :
const marker = L.marker(...
and refactor it inside
marker.on("click", function(e) {
const elem = document.getElementsByClassName(
`icon-marker-tooltip-${country}`
)[0];
const arr = elem.className.split(" ");
if (arr.indexOf(`mobile-active`) == -1) {
elem.className += " mobile-active";
}
});
return marker;
that's all for phone view mode 🎉
If we want to deploy our coronavirus map easily, without any server or any specific configuration - we can use Netlify
It supports Gatsby project without any further configuration
Let's start by running this command in the terminal
npm run buildbuy what happened ? Im sure your getting an error right now :
it turns out that using Odometer component doesn't support ssr, and Gatsby falis becuase of it.
lets look again in react-odometerjs package readme -
Because Odometer.js requires `document` object, we should load library using dynamic import, to avoid loading library on server-side.
so how we are going to do it in our Gatsby environment ?
Lets read how to dynamic import in Gatsby - gatsby plugin : loadable components ssr
first we start by installing the flowing packages
npm install --save gatsby-plugin-loadable-components-ssrThis plugin also requires @loadable/component as a peer dependency:
npm install --save @loadable/componentSimply add gatsby-plugin-loadable-components-ssr to the plugins array in gatsby-config.js.
// gatsby-config.js
module.exports = {
plugins: [
'gatsby-plugin-loadable-components-ssr',
// OR
{
resolve: `gatsby-plugin-loadable-components-ssr`,
options: {
// Whether replaceHydrateFunction should call ReactDOM.hydrate or ReactDOM.render
// Defaults to ReactDOM.render on develop and ReactDOM.hydrate on build
useHydrate: true,
},
}
],
}Now that our Gatsby environment is all ready, lets use loadable component in order to require react-odometerjs
In Section.js file , replace import react-odometerjs
import loadable from "@loadable/component";
const Odometer = loadable(() => import("react-odometerjs"));
Now try again to run
npm run buildyou'll get a successful message
Now all left to do is to push your code to git , and go to Netlify You will need to register and give it permissions to your repo in github.
Then in your page on Netlify click on new site from git :
Then choose Github option:
Now you will have to gibe Netlify permission to your github account , then choose your coronavirus map repo:
Netlify will know that your project is a Gatsby project, so you won't need to change any configuration, just click Deploy site
Now youll be redirected to page where you can see your build project status :
In the end you'll see that your project was successfully deployed 🎉