我们之前说过,前序遍历的 Morris 方法,如果已经掌握,今天中序遍历的 Morris 方法也就没有什么难度,仅仅修改了一丢丢。
我们先来回顾一下前序遍历 Morris 方法的代码部分。
前序遍历 Morris 代码
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return list;
}
TreeNode p1 = root; TreeNode p2 = null;
while (p1 != null) {
p2 = p1.left;
if (p2 != null) {
//找到左子树的最右叶子节点
while (p2.right != null && p2.right != p1) {
p2 = p2.right;
}
//添加 right 指针,对应 right 指针为 null 的情况
//标注 1
if (p2.right == null) {
list.add(p1.val);
p2.right = p1;
p1 = p1.left;
continue;
}
//对应 right 指针存在的情况,则去掉 right 指针
p2.right = null;
//标注2
} else {
list.add(p1.val);
}
//移动 p1
p1 = p1.right;
}
return list;
}
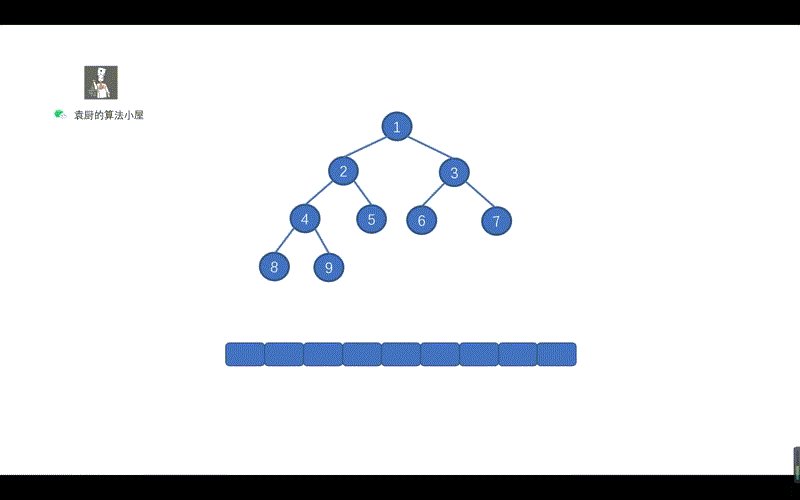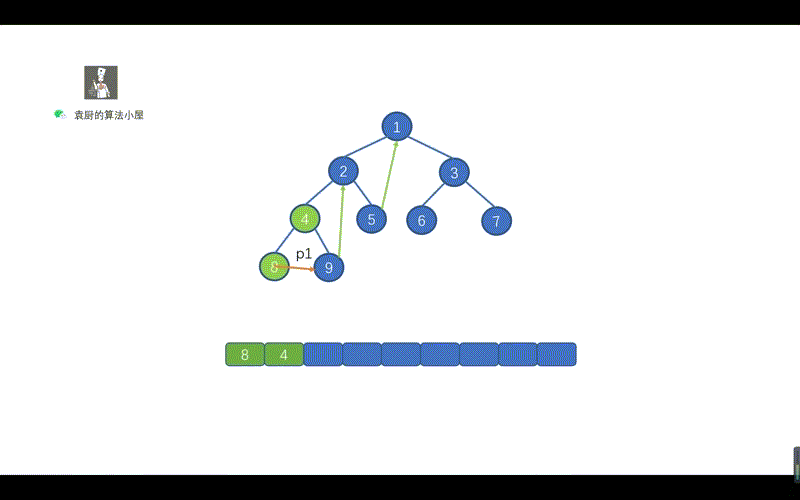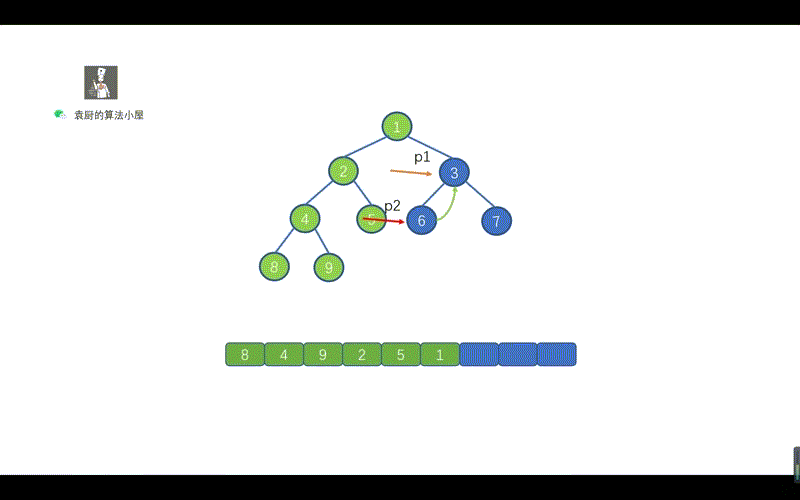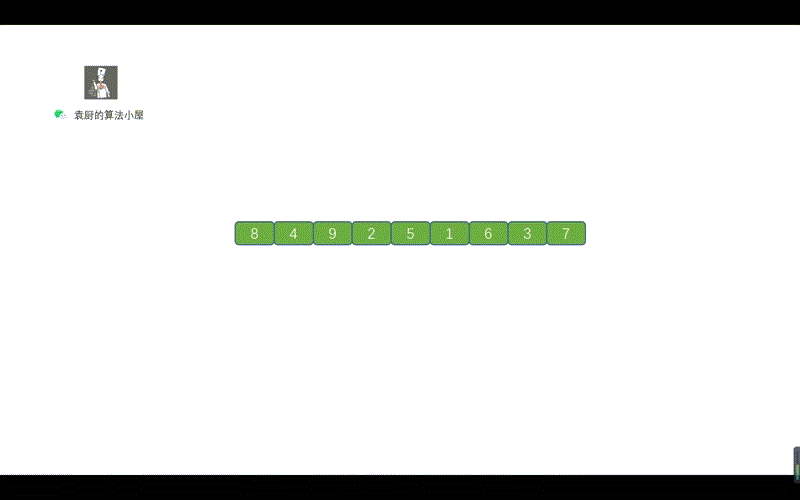
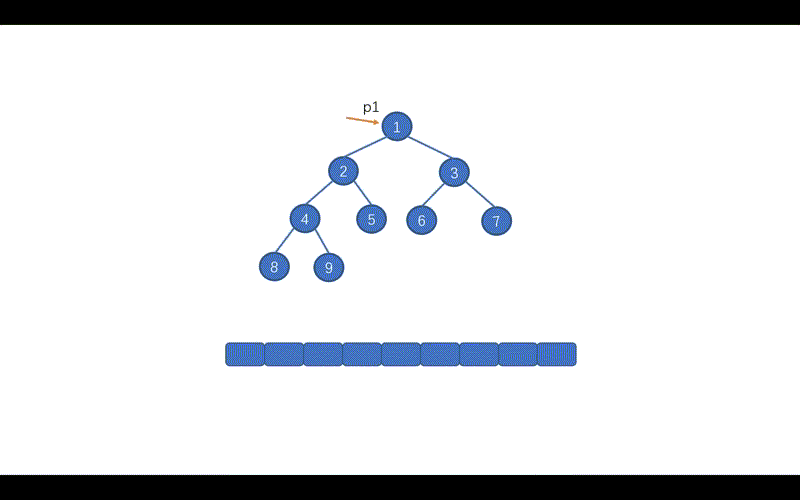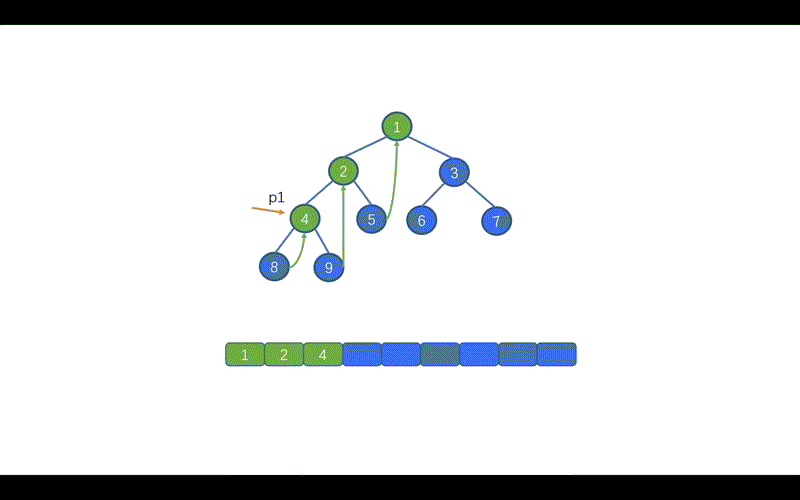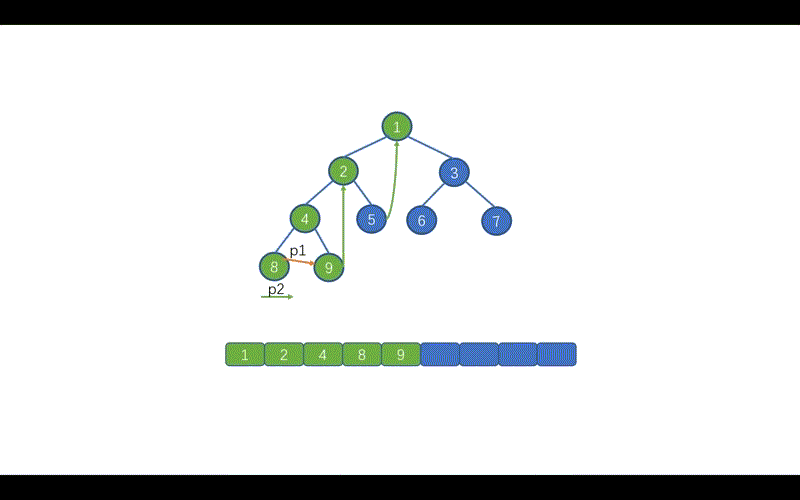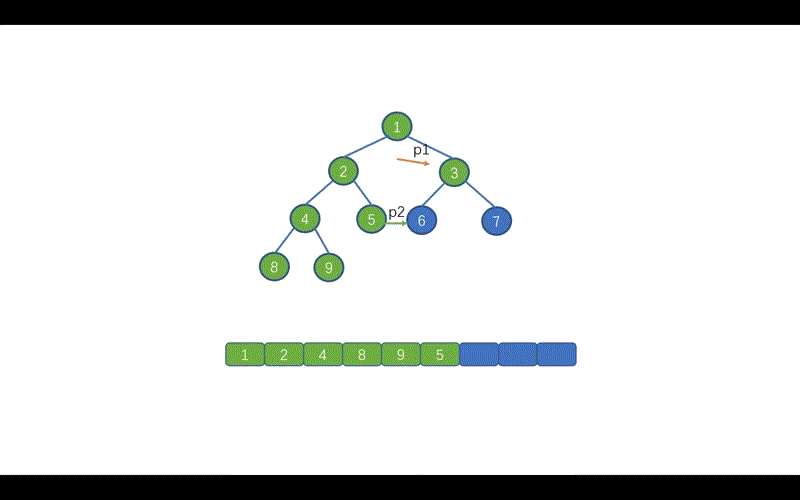
}我们先来看标注 1 的部分,这里的含义是,当找到 p1 指向节点的左子树中的最右子节点时。也就是下图中的情况,此时我们需要将 p1 指向的节点值,存入 list。
上述为前序遍历时的情况,那么中序遍历应该如何操作嘞。
前序遍历我们需要移动 p1 指针,p1 = p1.left 这样做的原因和上述迭代法原理一致,找到我们当前需要遍历的那个节点。
我们还需要修改哪里呢?见下图
我们在前序遍历时,遇到 p2.right == p1的情况时,则会执行 p2.right == null 并让 p1 = p1.right,这样做是因为,我们此时 p1 指向的值已经遍历完毕,为了防止重复遍历。
但是呢,在我们的中序 Morris 中我们遇到p2.right == p1此时 p1 还未遍历,所以我们需要在上面两条代码之间添加一行代码list.add(p1.val);
好啦,到这里我们就基本上就搞定了中序遍历的 Morris 方法,下面我们通过动画来加深一下印象吧,当然我也会把前序遍历的动画放在这里,大家可以看一下哪里有所不同。
参考代码:
//中序 Morris
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if (root == null) {
return list;
}
TreeNode p1 = root;
TreeNode p2 = null;
while (p1 != null) {
p2 = p1.left;
if (p2 != null) {
while (p2.right != null && p2.right != p1) {
p2 = p2.right;
}
if (p2.right == null) {
p2.right = p1;
p1 = p1.left;
continue;
} else {
p2.right = null;
}
}
list.add(p1.val);
p1 = p1.right;
}
return list;
}
}Swift Code:
class Solution {
func inorderTraversal(_ root: TreeNode?) -> [Int] {
var list:[Int] = []
guard root != nil else {
return list
}
var p1 = root, p2: TreeNode?
while p1 != nil {
p2 = p1!.left
if p2 != nil {
while p2!.right != nil && p2!.right !== p1 {
p2 = p2!.right
}
if p2!.right == nil {
p2!.right = p1
p1 = p1!.left
continue
} else {
p2!.right = nil
}
}
list.append(p1!.val)
p1 = p1!.right
}
return list
}
}