-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 3k
Quick Reference
##DEPRECATED WIKI PAGE!
###Use the shiny new ngdocs!
- ui-view
- autoscroll
- ui-sref - v0.2.0
- ui-sref-active - v0.2.6
- go() - v0.2.0
- transitionTo()
- reload()- v0.2.5
- includes()
- is()
- href() - v0.2.0
- get() - v0.2.0
- current
- note: using $state within templates
- sync() - v0.2.5
- isState - (v0.3)
- includedByState - (v0.3)
Be sure to include ui.router as a module dependency.
angular.module("myApp", ["ui.router"]).config(function($stateProvider){
$stateProvider.state(stateName, stateConfig);
})Creates a new application state. For alternate usage, see Object-based States
The parameters for .state() are:
String
A unique state name, e.g. "home", "about", "contacts". To create a parent/child state use a dot, e.g. "about.sales", "home.newest". Read more about nested states: Nested States & Nested Views
// The state() method takes a unique stateName (String) and a stateConfig (Object)
$stateProvider.state(stateName, stateConfig);
// stateName can be a single top-level name (must be unique).
$stateProvider.state("home", {});
// Or it can be a nested state name. This state is a child of the above "home" state.
$stateProvider.state("home.newest", {});
// Nest states as deeply as needed.
$stateProvider.state("home.newest.abc.xyz.inception", {});
// state() returns $stateProvider, so you can chain state declarations.
$stateProvider.state("home", {}).state("about", {}).state("contacts", {});Object
The stateConfig object has the following acceptable properties. This is just a reference, for usage and details please click the "Learn more..." links.
Three ways to set up your templates. Only use one per state (or view, see below)!
template String HTML content, or function that returns an HTML string
templateUrl String URL path to template file OR Function, returns URL path string
templateProvider Function, returns HTML content string
Learn more about state templates
A controller paired to the state
controller Function OR name as String
controllerProvider Function (injectable), returns the actual controller function or string.
A map of dependencies which should be injected into the controller
resolve Object
- keys - name of dependency to be injected into controller
- factory - {string|function} If string then it is alias for service. Otherwise if function, it is injected and return value it treated as dependency. If result is a promise, it is resolved before its value is injected into controller
A url with optional parameters. When a state is navigated or transitioned to, the $stateParams service will be populated with any parameters that were passed.
url String
Learn more about url routing with states
A map which optionally configures parameters declared in the url, or defines additional non-url parameters. Only use this within a state if you are not using url. Otherwise you can specify your parameters within the url. When a state is navigated or transitioned to, the $stateParams service will be populated with any parameters that were passed.
params Object
Learn more about parameters (examples are shown in url form, but they work just the same here)
Use the views property to set up multiple views. If you don't need multiple views within a single state this property is not needed. Tip: remember that often nested views are more useful and powerful than multiple sibling views.
views Object
- keys - {string} name of ui-view
- view config - {object} view configuration object can set up its own [templates] and (/~https://github.com/angular-ui/ui-router/wiki#the-simplest-form-of-state) [controllers].
Learn more about multiple named views
An abstract state will never be directly activated, but can provide inherited properties to its common children states.
abstract Boolean - (default is false)
Learn more about abstract states
Callback functions for when a state is entered and exited. Good way to trigger an action or dispatch an event, such as opening a dialog.
-
onEnterFunction, injected including resolves -
onExitFunction, injected including resolves
Learn more about state callbacks
Boolean (default true). If false will not retrigger the same state just because a search/query parameter has changed. Useful for when you'd like to modify $location.search() without triggering a reload.
Arbitrary data object, useful for custom configuration.
data Object
Learn more about attaching custom data to states
-
decorator(name, decorator)- Allows you to extend (carefully) or override (at your own peril) thestateBuilderobject used internally by$stateProvider. This can be used to add custom functionality to ui-router, for example inferring templateUrl based on the state name. -
decorator(name)- Returns the current (original or decorated) builder function that matchesname.
String
The name of the builder function to decorate. The builder functions that can be decorated are listed below. Though not all necessarily have a good use case for decoration, that is up to you to decide. To see the original code for each, see state.js - lines 7-108.
Existing builder functions and current return values:
-
parent- returns the parent state object. -
data- returns state data, including any inherited data that is not overridden by own values (if any). -
url- returns a UrlMatcher or null. -
navigable- returns closest ancestor state that has a URL (aka is navigable). -
params- returns an array of state params that are ensured to be a super-set of parent's params. -
views- returns a views object where each key is an absolute view name (i.e. "viewName@stateName") and each value is the config object (template, controller) for the view. Even when you don't use theviewsobject explicitly on a state config, one is still created for you internally. So by decorating this builder function you have access to decoratingtemplateandcontrollerproperties. -
ownParams- returns an array of params that belong to the state, not including any params defined by ancestor states. -
path- returns the full path from the root down to this state. Needed for state activation. -
includes- returns an object that includes every state that would pass a '$state.includes()' test.
In addition, users can attach custom decorators, which will generate new properties within the state's internal definition. There is currently no clear use-case for this beyond accessing internal states (i.e. $state.$current), however, expect this to become increasingly relevant as we introduce additional meta-programming features.
Warning: Decorators should not be interdependent because the order of execution of the builder functions in nondeterministic. Builder functions should only be dependent on the state definition object and super function.
Function
A function that is responsible for decorating the original builder function. The function receives two parameters:
-
state- The state config object. -
super- The original builder function.
Example Usage:
// Override the internal 'views' builder with a function that takes the state
// definition, and a reference to the internal function being overridden:
$stateProvider.decorator('views', function(state, parent) {
var result = {}, views = parent(state);
angular.forEach(views, function(config, name) {
var autoName = (state.name + "." + name).replace(".", "/");
config.templateUrl = config.templateUrl || "/partials/" + autoName + ".html";
result[name] = config;
});
return result;
});
$stateProvider.state("home", {
views: {
"contact.list": { controller: "ListController" },
"contact.item": { controller: "ItemController" }
}
});
// ...
$state.go("home");
// Auto-populates list and item views with /partials/home/contact/list.html,
// and /partials/home/contact/item.html, respectively.Redirects from one url to another.
String or RegExp or UrlMatcher
The incoming path that you want to redirect.
String
The path you want to redirect your user to.
Handles invalid routes by redirecting to the path provided.
String | Function
The path you want to redirect your user to.
For custom url handling.
Function
A function that takes in the $location as it's only argument. You are responsible for returning a valid path as a string.
The following directives are provided by the ui.router module.
The ui-view directive tells $state where to place your templates. A view can be unnamed or named.
<!-- Unnamed -->
<div ui-view></div>
<!-- Named -->
<div ui-view="viewName"></div>You can only have one unnamed view within any template (or root html). If you are only using a single view and it is unnamed then you can populate it like so:
<div ui-view></div> $stateProvider.state("home", {
template: "<h1>HELLO!</h1>"
})The above is equivalent to specifying your view explicity, by name, in this case an empty name:
$stateProvider.state("home", {
views: {
"": {
template: "<h1>HELLO!</h1>"
}
}
})But typically you'll only use the views property if you name your view or have more than one view in the same template. There's not really a compelling reason to name a view if its the only one, but you could if you wanted, like so:
<div ui-view="main"></div> $stateProvider.state("home", {
views: {
"main": {
template: "<h1>HELLO!</h1>"
}
}
})Really though, you'll use views to set up multiple views:
<div ui-view></div>
<div ui-view="chart"></div>
<div ui-view="data"></div> $stateProvider.state("home", {
views: {
"": {
template: "<h1>HELLO!</h1>"
},
"chart": {
template: "<chart_thing/>"
},
"data": {
template: "<data_thing/>"
}
}
})An attribute directive used on the ui-view element directive. It allows you to set the scroll behavior of the browser window when a view is populated. By default, $anchorScroll is overridden by ui-router's custom scroll service, $uiViewScroll. This custom service let's you scroll ui-view elements into view when they are populated during a state activation.
Note: To revert back to old $anchorScroll functionality, call $uiViewScrollProvider.useAnchorScroll().
Usage:
-
<ui-view autoscroll[='expression']/>- Addautoscrollattr toui-viewelement. Optionally use an expression to determine if the scroll is on or off.
Examples:
<!-- If autoscroll unspecified, then scroll ui-view into view
(Note: this default behavior is under review and may be reversed) -->
<ui-view/>
<!-- If autoscroll present with no expression,
then scroll ui-view into view -->
<ui-view autoscroll/>
<!-- If autoscroll present with valid expression,
then scroll ui-view into view if expression evaluates to true -->
<ui-view autoscroll='true'/>
<ui-view autoscroll='false'/>
<ui-view autoscroll='scopeVariable'/>A directive that binds a link (<a> tag) to a state. If the state has an associated URL, the directive will automatically generate & update the href attribute via the $state.href() method. Clicking the link will trigger a state transition with optional parameters. Also middle-clicking, right-clicking, and ctrl-clicking on the link will be handled natively by the browser.
Usage:
-
ui-sref='stateName'- Navigate to state, no params.'stateName'can be any valid absolute or relative state, following the same syntax rules as$state.go() -
ui-sref='stateName({param: value, param: value})'- Navigate to state, with params.
Example:
Template HTML:
<a ui-sref="home">Home</a> | <a ui-sref="about">About</a>
<ul>
<li ng-repeat="contact in contacts">
<a ui-sref="contacts.detail({ id: contact.id })">{{ contact.name }}</a>
</li>
</ul>Generated HTML (Html5Mode Off results in prepended '#'):
<a href="#/home" ui-sref="home">Home</a> | <a href="#/about" ui-sref="about">About</a>
<ul>
<li ng-repeat="contact in contacts">
<a href="#/contacts/1" ui-sref="contacts.detail({ id: contact.id })">Joe</a>
</li>
<li ng-repeat="contact in contacts">
<a href="#/contacts/2" ui-sref="contacts.detail({ id: contact.id })">Alice</a>
</li>
<li ng-repeat="contact in contacts">
<a href="#/contacts/3" ui-sref="contacts.detail({ id: contact.id })">Bob</a>
</li>
</ul>A note on relative ui-sref targets:
You can also use relative state paths within ui-sref, just like the relative paths passed to state.go(). You just need to be aware that the path is relative to the state that the link lives in, in other words the state that loaded the template containing the link.
A directive working alongside ui-sref to add classes to an element when the related ui-sref directive's state is active, and removing them when it is inactive. The primary use-case is to simplify the special appearance of navigation menus relying on ui-sref, by having the "active" state's menu button appear different, distinguishing it from the inactive menu items.
Usage:
-
ui-sref-active='class1 class2 class3'- classes "class1", "class2", and "class3" are each added to the directive element when the relatedui-sref's state is active, and removed when it is inactive.
Example:
Given the following template,
<ul>
<li ui-sref-active="active" class="item">
<a href ui-sref="app.user({user: 'bilbobaggins'})">@bilbobaggins</a>
</li>
<!-- ... -->
</ul>when the app state is "app.user", and contains the state parameter "user" with value "bilbobaggins", the resulting HTML will appear as
<ul>
<li ui-sref-active="active" class="item active">
<a ui-sref="app.user({user: 'bilbobaggins'})" href="/users/bilbobaggins">@bilbobaggins</a>
</li>
<!-- ... -->
</ul>The class name is interpolated once during the directives link time (any further changes to the interpolated value are ignored). Multiple classes may be specified in a space-separated format.
Use ui-sref-opts directive to pass options to $state.go(). Example:
<a ui-sref="home" ui-sref-opts="{reload: true}">Home</a>Returns a Promise representing the state of the transition.
Convenience method for transitioning to a new state. $state.go calls $state.transitionTo internally but automatically sets options to { location: true, inherit: true, relative: $state.$current, notify: true }. This allows you to easily use an absolute or relative to path and specify only the parameters you'd like to update (while letting unspecified parameters inherit from the current state).
String Absolute State Name or Relative State Path
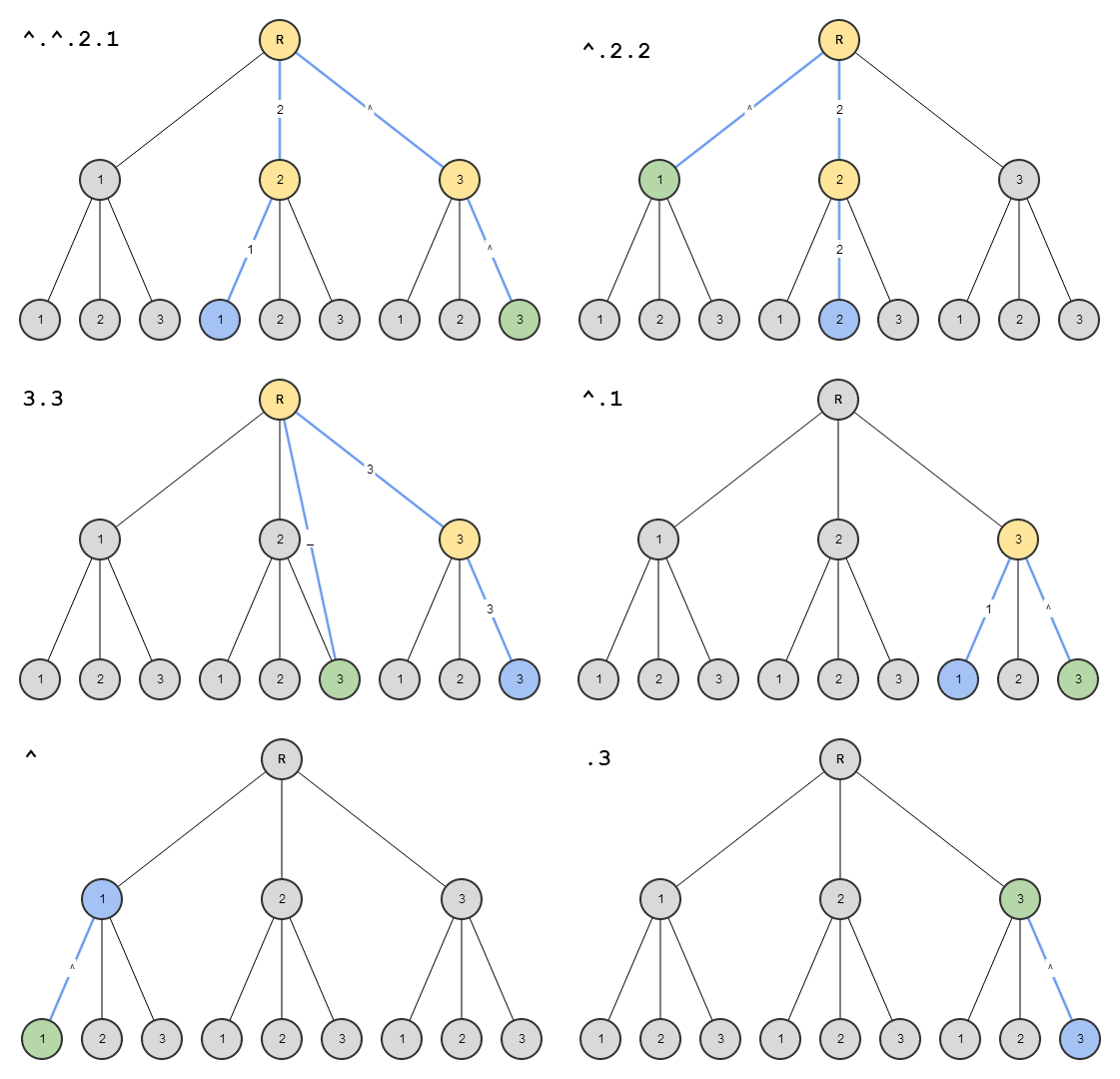
The name of the state that will be transitioned to or a relative state path. If the path starts with ^ or . then it is relative, otherwise it is absolute.
Some examples:
-
$state.go('contact.detail')will go to the 'contact.detail' state -
$state.go('^')will go to a parent state. -
$state.go('^.sibling')will go to a sibling state. -
$state.go('.child')will go to a child state. -
$state.go('.child.grandchild')will go to a grandchild state.
Object
A map of the parameters that will be sent to the state, will populate $stateParams.
Any parameters that are not specified will be inherited from currently defined parameters. This allows, for example, going to a sibling state that shares parameters specified in a parent state. Parameter inheritance only works between common ancestor states, I.e. transitioning to a sibling will get you the parameters for all parents, transitioning to a child will get you all current parameters, etc.
Object
If Object is passed, object is an options hash. The following options are supported:
-
locationBoolean or "replace" (default true), Iftruewill update the url in the location bar, iffalsewill not. If string"replace", will update url and also replace last history record. -
inheritBoolean (default true), Iftruewill inherit url parameters from current url. -
relativestateObject (default $state.$current), When transitioning with relative path (e.g '^'), defines which state to be relative from. -
notifyBoolean (default true), Iftruewill broadcast $stateChangeStart and $stateChangeSuccess events. -
reloadv0.2.5Boolean (default false), Iftruewill force transition even if the state or params have not changed, aka a reload of the same state. It differs from reloadOnSearch because you'd use this when you want to force a reload when everything is the same, including search params.
- Green = Starting State
- Yellow = Intermediary State
- Blue = Final Destination State
Returns a Promise representing the state of the transition.
Low-level method for transitioning to a new state. $state.go() uses transitionTo internally. $state.go() is recommended in most situations.
String
The name of the state that will be transitioned to.
Object
A map of the parameters that will be sent to the state, will populate $stateParams.
Object
Object is an options hash. The following options are supported:
-
locationBoolean or "replace" (default true), Iftruewill update the url in the location bar, iffalsewill not. If string"replace", will update url and also replace last history record. -
inheritBoolean (default false), Iftruewill inherit url parameters from current url. -
relativestateObject (default null), When transitioning with relative path (e.g '^'), defines which state to be relative from. -
notifyBoolean (default true), Iftruewill broadcast $stateChangeStart and $stateChangeSuccess events. -
reloadv0.2.5Boolean (default false), Iftruewill force transition even if the state or params have not changed, aka a reload of the same state. It differs from reloadOnSearch because you'd use this when you want to force a reload when everything is the same, including search params.
Returns null
A method that force reloads the current state. All resolves are re-resolved, events are not re-fired, and controllers reinstantiated (bug with controllers reinstantiating right now, fixing soon).
This is just an alias for:
$state.transitionTo($state.current, $stateParams, {
reload: true, inherit: false, notify: false
});Returns Boolean
A method to determine if the current active state is equal to or is the child of the state stateName. If any params are passed then they will be tested for a match as well. Not all the parameters need to be passed, just the ones you'd like to test for equality.
String
A partial name to be searched for within the current state name. For example, if you had the following states set up:
- contacts
- contacts.list
- contacts.details
- contacts.details.item
- about
So, e.g. if you were within contacts.details.item then:
$state.includes("contacts"); // returns true
$state.includes("contacts.details"); // returns true
$state.includes("contacts.details.item"); // returns true
$state.includes("contacts.list"); // returns false
$state.includes("about"); // returns falseObject
A param object, e.g. {sectionId: section.id}, that you'd like to test against the current active state.
Let's say the current active state was "contacts.details.item.edit" activated by a url of "/contacts/1/address/edit", where 1 populates the :id param and 'address' populates the :item param. So then:
$state.includes("contacts.detail", {id: 1}); // returns true
$state.includes("contacts.detail.item", {item:'address'}); // returns true
$state.includes("contacts", {bogus:'gnarly'}); // returns falseReturns Boolean
Similar to includes, but only checks for the full state name. If params is supplied then it will be tested for strict equality against the current active params object, so all params must match with none missing and no extras.
String or Object
The state name or state object you'd like to check.
So, e.g. if you were within contact.details.item then:
$state.is("contact.details.item"); // returns true
$state.is(contactDetailItemStateConfigObj); // returns true
// Everything else would return falseObject
A param object, e.g. {sectionId: section.id}, that you'd like to test against the current active state.
Let's say the current active state was "contacts.details.item.edit" activated by a url of "/contacts/1/address/edit", where 1 populates the :id param and 'address' populates the :item param. So then:
$state.includes("contacts.detail.item.edit", {id: 1, item: 'address'}); // returns true
// Everything else returns `false`Returns String Compiled URL
A url generation method that returns the compiled url for the given state populated with the given params.
e.g. expect($state.href("about.person", { person: "bob" })).toEqual("/about/bob");
Note: returns null if no valid url can be constructed.
String or Object
The state name or state object you'd like to generate a url from.
Object
An object of parameter values to fill the state's required parameters.
Object
An options hash, the following options are available:
-
lossyBoolean (default true) If true, and if there is no url associated with the state provided in the first parameter, then the constructed href url will be built from the first navigable ancestor (aka ancestor with a valid url). -
inheritBoolean (default false) Iftruewill inherit url parameters from current url. -
relativestateObject (default $state.$current), When transitioning with relative path (e.g '^'), defines which state to be relative from. -
absoluteBoolean (default false) Iftruewill generate an absolute url, e.g."http://www.example.com/fullurl".
Returns Object
-
get(stateName)- A method for retrieving the configuration object for any state, by passing the name as a string. -
get()-v0.3.0- Returns an array of all state config objects.
String
The name of the state for which you'd like to get the original state configuration object for.
Returns State Object
A reference to the state's config object. However you passed it in. Useful for accessing custom data.
Learn More about the state config object
Since its very common to access $state in your templates, you need to bind $state to $rootScope (or any other accessible scope) to access it from a template/view. Typically you can do this on module run:
angular.module("myApp").run(function ($rootScope, $state, $stateParams) {
$rootScope.$state = $state;
$rootScope.$stateParams = $stateParams;
});Now you can access state within a template:
<ul class="nav">
<li ng-class="{ active: $state.includes('contacts') }"><a href="#/contacts">Contacts</a></li>
<li ng-class="{ active: $state.includes('about') }"><a href="#/about">About</a></li>
</ul>Returns null.
Triggers an update; the same update that happens when the address bar url changes, aka $locationChangeSuccess. This method is useful when you need to use preventDefault() on the $locationChangeSuccess event, perform some custom logic (route protection, auth, config, redirection, etc) and then finally proceed with the transition by calling $urlRouter.sync().
angular.module('app', ['ui.router']);
.run(function($rootScope, $urlRouter) {
$rootScope.$on('$locationChangeSuccess', function(evt) {
// Halt state change from even starting
evt.preventDefault();
// Perform custom logic
var meetsRequirement = /* ... */
// Continue with the update and state transition if logic allows
if (meetsRequirement) $urlRouter.sync();
});
});A service that is populated by the current state's parameters. Useful for injecting into your own controllers or services to access the parameters. It will have one key per url parameter.
Note: it must be injected into a controller directly attached to the desired state
A small service that handles the scrolling behind the scenes for the autoscroll attribute directive. You can also use it if you'd like.
When called with a jqLite element, it scrolls the element into view (after a $timeout so the DOM has time to refresh). If you prefer to rely on $anchorScroll to scroll the view to the anchor, this can be enabled by calling $uiViewScrollProvider.useAnchorScroll().
Usage:
-
$uiViewScroll(elem)- will scrolleleminto view
Handy filters to use together with other angular.js directives (ng-class, ng-if.. and so on).
"stateName" | isState - Translates to $state.is("stateName")
"stateName" | includedByState - Translates to $state.includes("stateName")
All these events are broadcast from the $rootScope.
-
$stateChangeSuccess- fired once the state transition is complete. -
$stateChangeStart- fired when the transition begins. -
$stateNotFound- fired when a state cannot be found by its name. -
$stateChangeError- fired when an error occurs during transition.
Learn more about State Change Events
-
$viewContentLoading- fired once per view when the view begins loading (before DOM is rendered). Broadcast from$rootScope. -
$viewContentLoaded- fired once per view when the view is loaded (after DOM is rendered). Emitted from view's$scope.