-
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 332
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
docs(token-auth-keycloak): add tutorial for the example
- Loading branch information
Showing
8 changed files
with
147 additions
and
4 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,137 @@ | ||
| # Token Authentication with Keycloak | ||
|
|
||
| In this example, we'll see how to configure your keycloak server and use token authentication with your registry. This will use the [docker registry v2 token authentication protocol](https://docs.docker.com/registry/spec/auth/token/). | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| In this image, we will replace the docker client/daemon by the Docker Registry UI. Here are the steps: | ||
|
|
||
| 1. Attempt to get a resource (catalog, image info, image delete) with the registry. | ||
| 2. If the registry requires authorization it will return a `401 Unauthorized` HTTP response with information on how to authenticate. | ||
| 3. The **docker registry ui** makes a request to **keycloak** for a Bearer token. | ||
| 1. Your browser will use the [Basic Access Authentication Protocol](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Basic_access_authentication#Protocol). But keycloak does not support this protocol... That's why we need a nginx proxy on top of keycloak. | ||
| 2. Your proxy will receive a request on `/auth/realms/{realm name}/protocol/docker-v2/auth` without `Authentication` header. It will return a `401 Unauthorized` HTTP response with `WWW-Authenticate` header. | ||
| 3. Your browser will ask you your credentials. | ||
| 4. The proxy will pass the credentials to keycloak. | ||
| 4. Keycloak returns an opaque Bearer token representing the client’s authorized access. | ||
| 5. The **docker registry ui** retries the original request with the Bearer token embedded in the request’s Authorization header. | ||
| 6. The Registry authorizes the client by validating the Bearer token and the claim set embedded within it and begins the session as usual. | ||
|
|
||
| :warning: If you are configuring from scratch your own keycloak server, remove files in `data` folder first with certificates in `conf/registry/localhost.*` | ||
|
|
||
| ## Configure your nginx/proxy server | ||
|
|
||
| I will highlight required configuration for Basic Access Authentication Protocol. Replace the `{realm name}` by the name of your realm. In my example the realm is master, but you should create your own realm for your users. | ||
|
|
||
| ```nginx | ||
| resolver 127.0.0.11 valid=30s; | ||
| set $keycloak "http://keycloak:8080"; | ||
| # Location to get keycloak token | ||
| location /auth/realms/{realm name}/protocol/docker-v2/auth { | ||
| proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme; | ||
| proxy_set_header Host $host; | ||
| proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $host; | ||
| # By default, keycloak returns 400 instead of 401, we need to change that | ||
| if ($http_authorization = "") { | ||
| add_header WWW-Authenticate 'Basic realm="Keycloak login"' always; | ||
| return 401; | ||
| } | ||
| proxy_pass $keycloak; | ||
| } | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| Start your nginx server. It will be available on http://localhost/ in my example. | ||
|
|
||
| ```sh | ||
| docker-compose up -d proxy | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ## Configure your keycloak server | ||
|
|
||
| I will highlight required configuration for docker protocol. You will need to add this option to your keycloak command line: | ||
|
|
||
| ``` | ||
| -Dkeycloak.profile.feature.docker=enabled | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| Then the defalt user can be configured via environment variables | ||
| ```yml | ||
| services: | ||
| keycloak: | ||
| image: jboss/keycloak | ||
| environment: | ||
| KEYCLOAK_USER: admin | ||
| KEYCLOAK_PASSWORD: password | ||
| user: root | ||
| networks: | ||
| - registry-ui-net | ||
| command: -Dkeycloak.profile.feature.docker=enabled -b 0.0.0.0 | ||
| ``` | ||
| Now you can start your keycloak server, it will be available on http://localhost/auth in my example. | ||
| ```sh | ||
| docker-compose up -d keycloak | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| Now you need to configure your docker client with these steps: | ||
|
|
||
| Go to the keycloak home page: http://localhost/auth and click on `Administration Console`. | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| Sign in with your login and password (in my example it's `admin` and `password`). | ||
|
|
||
| 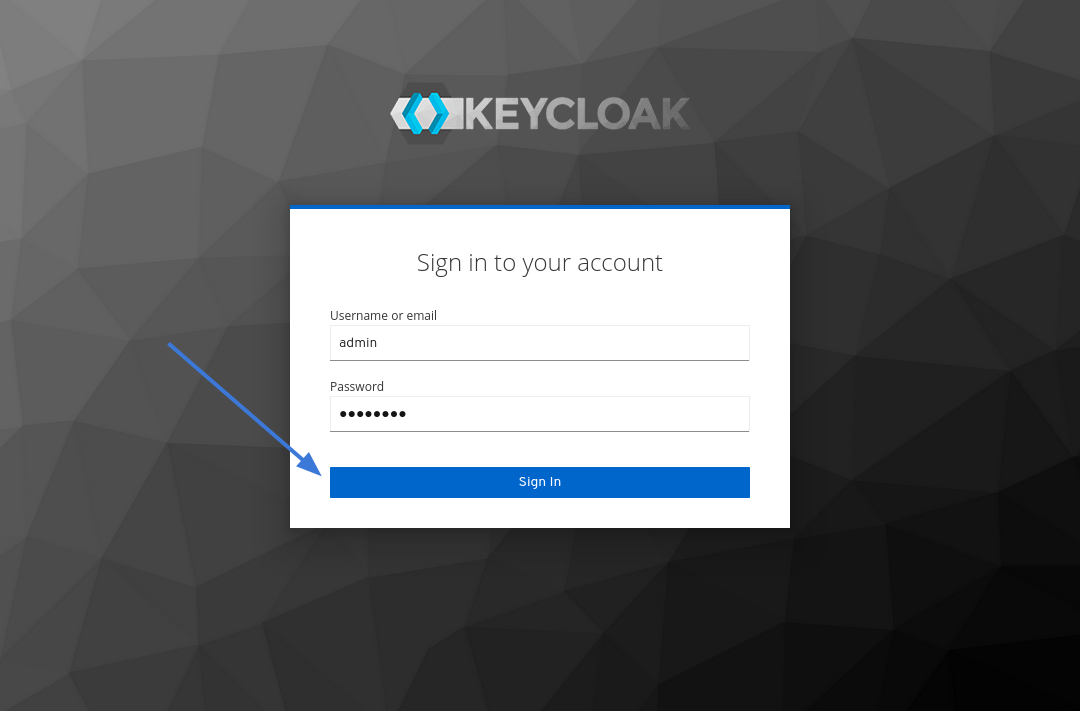 | ||
|
|
||
| Go to `Clients` in the left side menu. | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| Create a new client. | ||
|
|
||
| 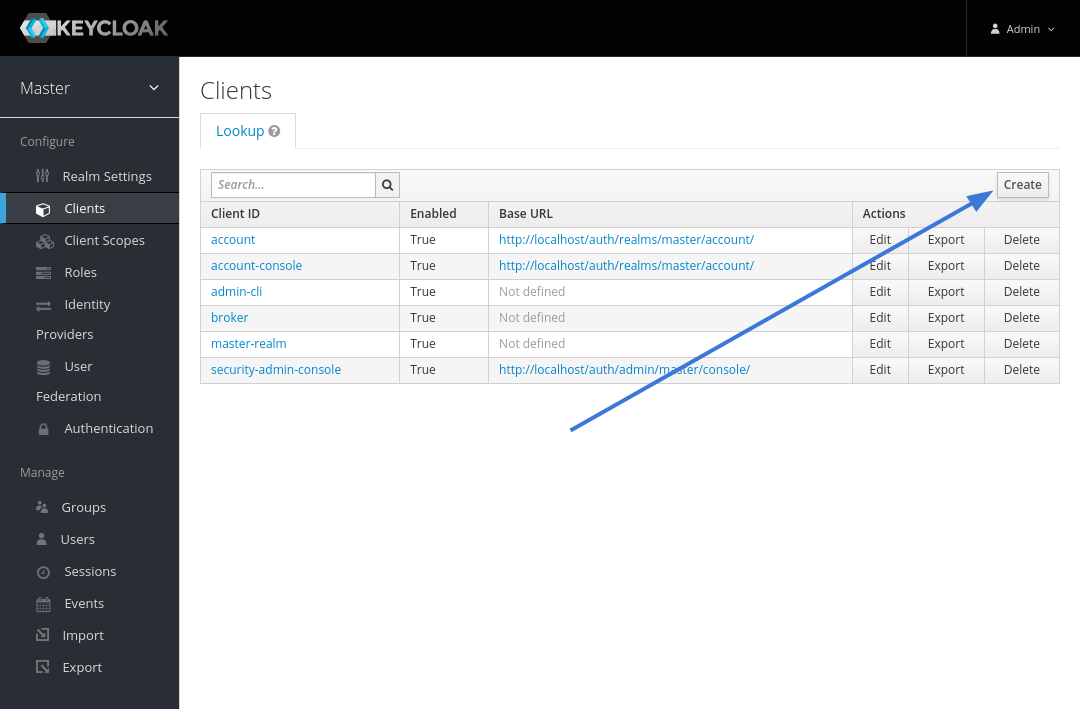 | ||
|
|
||
| Enter a name for `Client ID`, choose `docker-v2` as the `Client Protocol`, and click `Save`. | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| Navigate to `Installation` tab, choose `Docker Compose YAML` as `Format Option` and click `Download` | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| When you extract the archive, the resulting directory should look like this. | ||
|
|
||
| ``` | ||
| keycloak-docker-compose-yaml | ||
| ├── certs | ||
| │ ├── localhost.crt | ||
| │ ├── localhost.key | ||
| │ └── localhost_trust_chain.pem | ||
| ├── data | ||
| ├── docker-compose.yaml | ||
| └── README.md | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| Copy all the files from `certs` folder to `conf/registry` (this will replace files generated for this example). | ||
|
|
||
| ## Configure your registry server | ||
|
|
||
| The last step is the configuration of your registry server. The config file is located in `conf/registry/config.yml`. The import part of the configuration is `auth.token` where you need to set `realm`, `service`, `issuer` and the `rootcertbundle` from the previous archive. | ||
|
|
||
| ```yml | ||
| auth: | ||
| token: | ||
| realm: http://localhost/auth/realms/{realm name}/protocol/docker-v2/auth | ||
| service: docker-registry | ||
| issuer: http://localhost/auth/realms/{realm name} | ||
| rootcertbundle: /etc/docker/registry/localhost_trust_chain.pem | ||
| ``` | ||
| Now you can start your docker registry with your docker registry ui. | ||
| ```sh | ||
| docker-compose up -d registry ui | ||
| ``` |
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
Loading
Sorry, something went wrong. Reload?
Sorry, we cannot display this file.
Sorry, this file is invalid so it cannot be displayed.
Loading
Sorry, something went wrong. Reload?
Sorry, we cannot display this file.
Sorry, this file is invalid so it cannot be displayed.
Loading
Sorry, something went wrong. Reload?
Sorry, we cannot display this file.
Sorry, this file is invalid so it cannot be displayed.
Loading
Sorry, something went wrong. Reload?
Sorry, we cannot display this file.
Sorry, this file is invalid so it cannot be displayed.
Loading
Sorry, something went wrong. Reload?
Sorry, we cannot display this file.
Sorry, this file is invalid so it cannot be displayed.
Loading
Sorry, something went wrong. Reload?
Sorry, we cannot display this file.
Sorry, this file is invalid so it cannot be displayed.