Binary Search is a searching algorithm that finds the position of a target value within a sorted array.
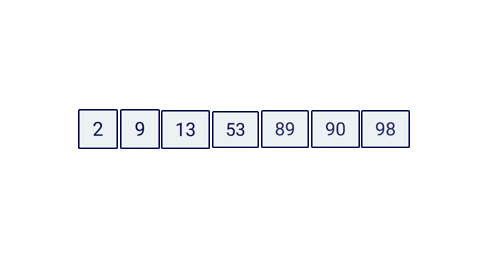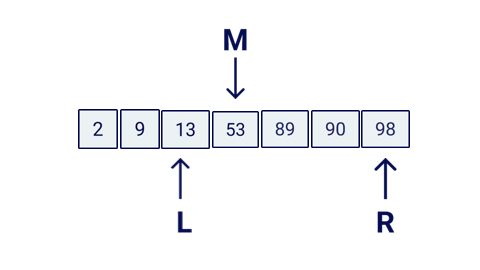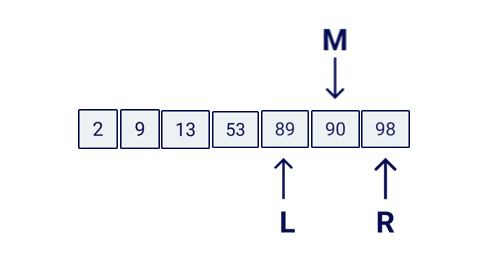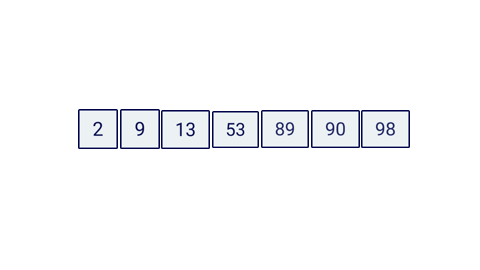
Binary Search compares the target value to the middle element of the array. If they are not equal, the half in which the target cannot lie is eliminated and the search continues on the remaining half, again taking the middle element to compare to the target value, and repeating this until the target value is found.
If the search ends with the remaining half being empty, the target is not in the array.
The time complexity of this algorithm is O(log n).
A = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
x = 5
Step 1: Set lower bound to 0
Step 2: Set upper bound to n-1
Step 3: If x > A[n-1] or x < A[0] then print element not found
Step 4: Set mid to the lower bound plus upper bound divided by 2
Step 5: If A[mid] < x then set lower bound to mid + 1
Step 6: Else if A[mid] > x then set upper bound to mid - 1
Step 7: Else if A[mid] = x then print element found at index mid
Step 8: If lower bound > upper bound then print element not found
Step 9: Go to step 4
procedure binary_search (list, value)
let min = 0
let max = length of list - 1
let mid
while min <= max
set mid to the average of min and max, rounded down (so that it is an integer)
if list[mid] < value
set min to mid + 1
else if list[mid] > value
set max to mid - 1
else
return mid
end if
end while
return not found
end procedure
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdio.h>
void BinarySearch(int arr[], int n, int x)
{
int low = 0;
int high = n;
int mid;
// If x is greater than the last element or less than the first element, element not found
while(low <= high)
{
mid = (low + high)/2; // Set mid to the lower bound plus upper bound divided by 2
if(arr[mid] == x) // If element is found, print index
{
printf("Element found at index %d", mid+1);
return;
}
else if(arr[mid] < x) // If element is greater than mid, set lower bound to mid + 1
{
low = mid + 1;
}
else // If element is less than mid, set upper bound to mid - 1
{
high = mid - 1;
}
}
printf("Element not found");
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = {10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 55, 60};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
int x = 30;
BinarySearch(arr, n, x);
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void BinarySearch(int arr[], int n, int x)
{
int low = 0;
int high = n;
int mid;
// If x is greater than the last element or less than the first element, element not found
while(low <= high)
{
mid = (low + high)/2; // Set mid to the lower bound plus upper bound divided by 2
if(arr[mid] == x) // If element is found, print index
{
cout << "Element found at index " << mid+1;
return;
}
else if(arr[mid] < x) // If element is greater than mid, set lower bound to mid + 1
{
low = mid + 1;
}
else // If element is less than mid, set upper bound to mid - 1
{
high = mid - 1;
}
}
cout << "Element not found";
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = {10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 55, 60};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
int x = 30;
BinarySearch(arr, n, x);
return 0;
}public class BinarySearch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 55, 60};
int n = arr.length;
int x = 30;
BinarySearch(arr, n, x);
}
public static void BinarySearch(int[] arr, int n, int x) {
int low = 0;
int high = n;
int mid;
// If x is greater than the last element or less than the first element, element not found
while(low <= high) {
mid = (low + high)/2; // Set mid to the lower bound plus upper bound divided by 2
if(arr[mid] == x) { // If element is found, print index
System.out.println("Element found at index " + (mid+1));
return;
}
else if(arr[mid] < x) { // If element is greater than mid, set lower bound to mid + 1
low = mid + 1;
}
else { // If element is less than mid, set upper bound to mid - 1
high = mid - 1;
}
}
System.out.println("Element not found");
}
}def BinarySearch(arr, n, x):
low = 0
high = n
# If x is greater than the last element or less than the first element, element not found
while low <= high:
mid = (low + high)//2 # Set mid to the lower bound plus upper bound divided by 2
if arr[mid] == x: # If element is found, print index
print("Element found at index " + str(mid+1))
return
elif arr[mid] < x: # If element is greater than mid, set lower bound to mid + 1
low = mid + 1
else: # If element is less than mid, set upper bound to mid - 1
high = mid - 1
print("Element not found")
arr = [10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 55, 60]
n = len(arr)
x = 30
BinarySearch(arr, n, x)