New maintainer wanted! I will no longer use Deye devices. Partly because of the #RelaisGate.
Get information from Deye Microinverter
The whole thing is just a learning exercise for now. We will see.
- clone the sources
- Bootstrap and create default user settings by just call
./cli.py edit-settings - Change the settings for your needs
- ...use the commands... ;)
- Setup systemd service to publish the inventer values to a Home Assistant instance via MQTT
Currently just clone the project and just start the cli (that will create a virtualenv and installs every dependencies)
Note: Please enable https://www.piwheels.org/ if you are on a Raspberry Pi !
e.g.:
~$ git clone /~https://github.com/jedie/inverter-connect.git
~$ cd inverter-connect
~/inverter-connect$ ./cli.py --helpThe output of ./cli.py --help looks like:
Usage: ./cli.py [OPTIONS] COMMAND [ARGS]...
╭─ Options ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╮
│ --help Show this message and exit. │
╰──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯
╭─ Commands ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╮
│ debug-settings Display (anonymized) MQTT server username and password │
│ edit-settings Edit the settings file. On first call: Create the default one. │
│ inverter-version Print all version information of the inverter │
│ print-at-commands Print one or more AT command values from Inverter. │
│ print-values Print all known register values from Inverter, e.g.: │
│ publish-loop Publish current data via MQTT for Home Assistant (endless loop) │
│ read-register Read register(s) from the inverter │
│ set-time Set current date time in the inverter device. │
│ systemd-debug Print Systemd service template + context + rendered file content. │
│ systemd-remove Write Systemd service file, enable it and (re-)start the service. (May │
│ need sudo) │
│ systemd-setup Write Systemd service file, enable it and (re-)start the service. (May │
│ need sudo) │
│ systemd-status Display status of systemd service. (May need sudo) │
│ systemd-stop Stops the systemd service. (May need sudo) │
│ test-mqtt-connection Test connection to MQTT Server │
│ version Print version and exit │
╰──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯
Update your settings via: ./cli.py edit-settings and insert MQTT credentials in section [mqtt]
Check also the config section [systemd] and [systemd.template_context]
but normally they must not be changed ;)
To verify your settings, call: ./cli.py debug-settings
To see the systemd service file content, just call: ./cli.py systemd-debug
Note: Some of the systemd commands, needs sudo because a normal user can't change systemd services!
You will see permission errors with a hint to call the cli with sudo ;)
If everything looks okay, setup and start the systemd service with: sudo ./cli.py systemd-setup
Check the services with: sudo ./cli.py systemd-status
Help from ./cli.py print-values --help Looks like:
Usage: ./cli.py publish-loop [OPTIONS]
Publish current data via MQTT for Home Assistant (endless loop)
The "Daily Production" count will be cleared in the night, by set the current date time via
AT-command.
╭─ Options ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╮
│ * --ip TEXT IP address of your inverter [required] │
│ * --port INTEGER Port of inverter services │
│ [default: 48899] │
│ [required] │
│ * --inverter [deye_2mppt|deye_4mppt|deye_sg04lp3] Prefix of yaml config files in │
│ inverter/definitions/ │
│ [default: deye_2mppt] │
│ [required] │
│ --verbosity -v INTEGER RANGE [0<=x<=3] Verbosity level; Accepts integer value │
│ e.g.: "--verbose 2" or can be count │
│ e.g.: "-vv" │
│ [default: 0; 0<=x<=3] │
│ --help Show this message and exit. │
╰──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯
Help from ./cli.py print-values --help Looks like:
Usage: ./cli.py print-values [OPTIONS]
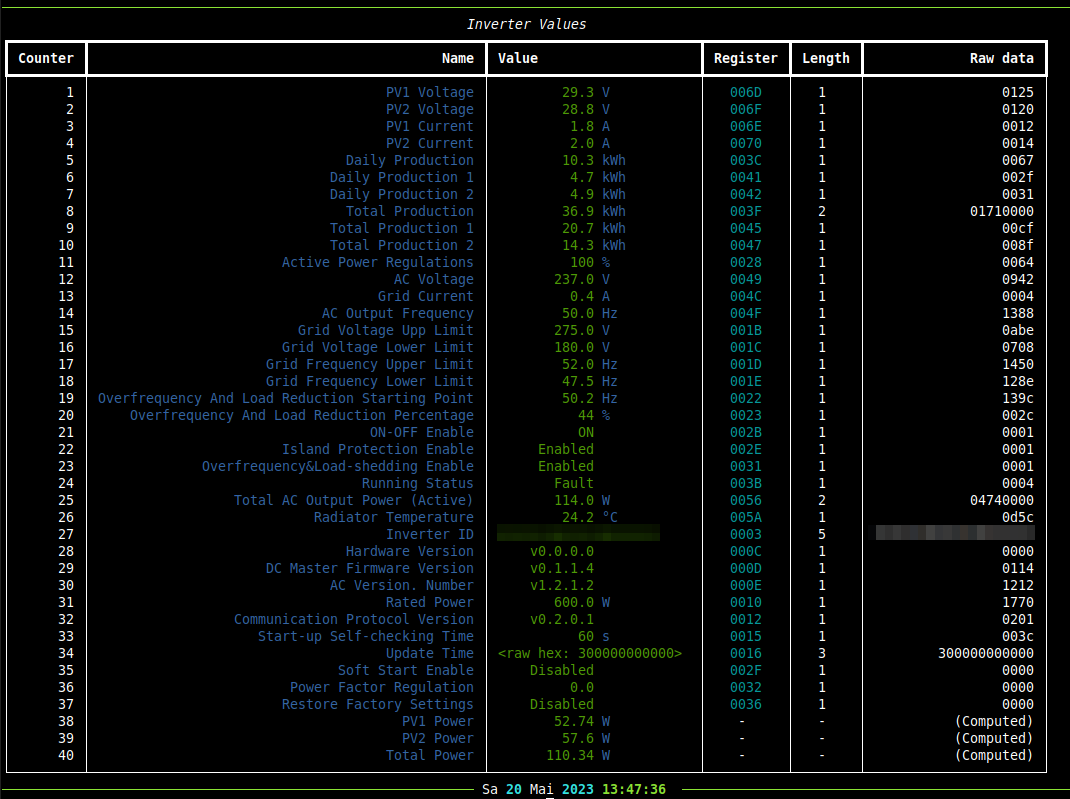
Print all known register values from Inverter, e.g.:
.../inverter-connect$ ./cli.py print-values
╭─ Options ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╮
│ * --ip TEXT IP address of your inverter [required] │
│ * --port INTEGER Port of inverter services │
│ [default: 48899] │
│ [required] │
│ * --inverter [deye_2mppt|deye_4mppt|deye_sg04lp3] Prefix of yaml config files in │
│ inverter/definitions/ │
│ [default: deye_2mppt] │
│ [required] │
│ --verbosity -v INTEGER RANGE [0<=x<=3] Verbosity level; Accepts integer value │
│ e.g.: "--verbose 2" or can be count │
│ e.g.: "-vv" │
│ [default: 0; 0<=x<=3] │
│ --compact -c Only show the values concerning power │
│ generation │
│ --help Show this message and exit. │
╰──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯
Example output of print-values call:
Help from ./cli.py print-at-commands --help Looks like:
Usage: ./cli.py print-at-commands [OPTIONS] [COMMANDS]...
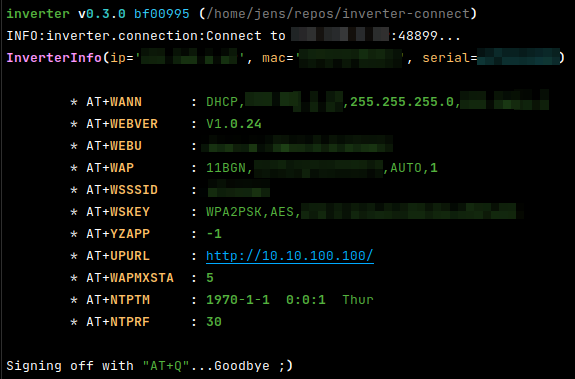
Print one or more AT command values from Inverter.
Use all known AT commands, if no one is given, e.g.:
.../inverter-connect$ ./cli.py print-at-commands
Or specify one or more AT-commands, e.g.:
.../inverter-connect$ ./cli.py print-at-commands WEBVER .../inverter-connect$ ./cli.py
print-at-commands WEBVER WEBU
e.g.: Set NTP server, enable NTP and check the values:
.../inverter-connect$ ./cli.py print-at-commands NTPSER=192.168.1.1 NTPEN=on NTPSER NTPEN
wait a while and request the current date time:
.../inverter-connect$ ./cli.py print-at-commands NTPTM
(Note: The prefix "AT+" will be added to every command)
╭─ Options ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╮
│ * --ip TEXT IP address of your inverter [required] │
│ * --port INTEGER Port of inverter services [default: 48899] │
│ [required] │
│ --verbosity -v INTEGER RANGE [0<=x<=3] Verbosity level; Accepts integer value e.g.: │
│ "--verbose 2" or can be count e.g.: "-vv" │
│ [default: 0; 0<=x<=3] │
│ --help Show this message and exit. │
╰──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯
Example output of print-at-commands call:
Help from ./cli.py read-register --help Looks like:
Usage: ./cli.py read-register [OPTIONS] REGISTER LENGTH
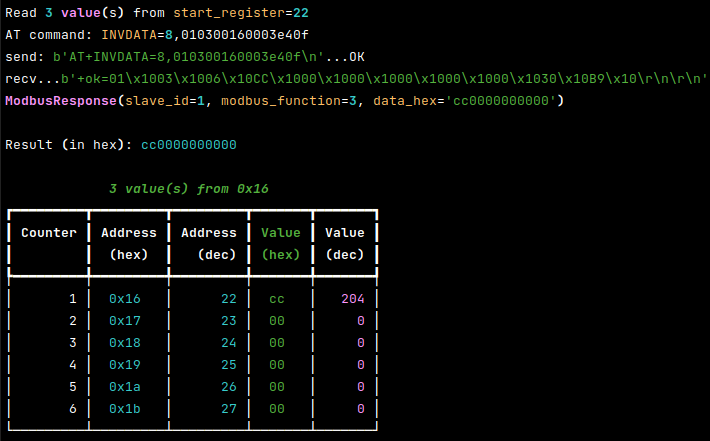
Read register(s) from the inverter
e.g.: read 3 registers starting from 0x16:
.../inverter-connect$ ./cli.py read-register 0x16 3
e.g.: read the first 32 registers:
.../inverter-connect$ ./cli.py read-register 0 32
The start address can be pass as decimal number or as hex string, e.g.: 0x123
╭─ Options ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╮
│ * --ip TEXT IP address of your inverter [required] │
│ * --port INTEGER Port of inverter services [default: 48899] │
│ [required] │
│ --verbosity -v INTEGER RANGE [0<=x<=3] Verbosity level; Accepts integer value e.g.: │
│ "--verbose 2" or can be count e.g.: "-vv" │
│ [default: 0; 0<=x<=3] │
│ --help Show this message and exit. │
╰──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯
Example output of read-register call:
For development, we have a separate CLI, just call it:
~/inverter-connect$ ./dev-cli.py --helpThe output of ./dev-cli.py --help looks like:
Usage: ./dev-cli.py [OPTIONS] COMMAND [ARGS]...
╭─ Options ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╮
│ --help Show this message and exit. │
╰──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯
╭─ Commands ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╮
│ check-code-style Check code style by calling darker + flake8 │
│ coverage Run and show coverage. │
│ create-default-settings Create a default user settings file. (Used by CI pipeline ;) │
│ fix-code-style Fix code style of all inverter source code files via darker │
│ install Run pip-sync and install 'inverter' via pip as editable. │
│ mypy Run Mypy (configured in pyproject.toml) │
│ publish Build and upload this project to PyPi │
│ safety Run safety check against current requirements files │
│ test Run unittests │
│ tox Run tox │
│ update Update "requirements*.txt" dependencies files │
│ update-test-snapshot-files Update all test snapshot files (by remove and recreate all snapshot │
│ files) │
│ version Print version and exit │
╰──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯
Others before me have done good work. In particular, I have learned a lot from the following projects:
- /~https://github.com/s10l/deye-logger-at-cmd
- /~https://github.com/kbialek/deye-inverter-mqtt
- /~https://github.com/StephanJoubert/home_assistant_solarman
The included definitions yaml files are from: